2gnx Results: Difference between revisions
| (61 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Evolutionary analysis== | |||
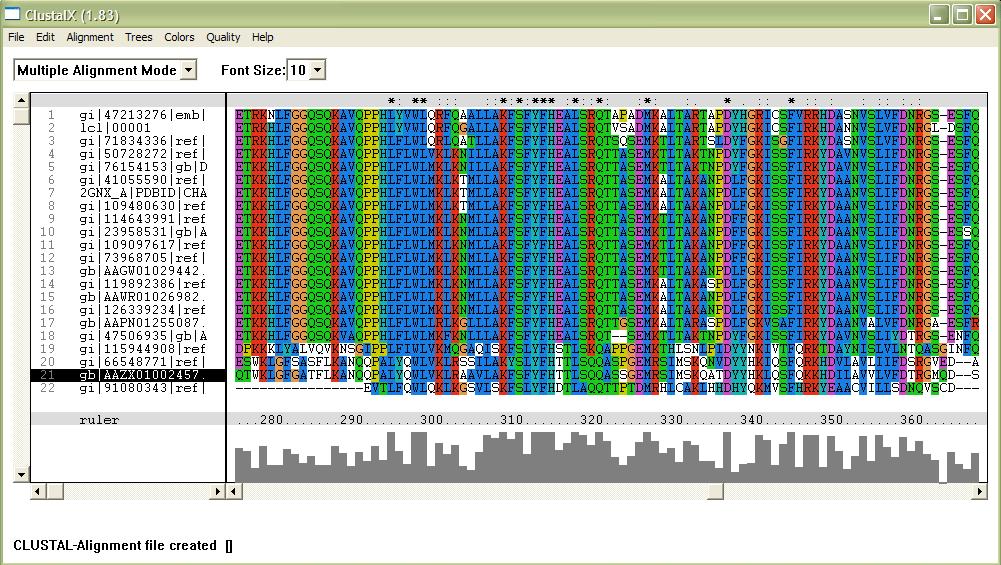
[[Image:alignment.jpg|framed|'''Figure 1'''<BR>This image shows part of a complete alignment of the sequences used. Asterisks (*) indicate residues that are conserved across all sequences, and colons (:) indicate partial conservation across all sequences.|none]]<BR> | |||
[[Image:tree1.jpg|framed|'''Figure 2'''<BR>The phylogenetic tree shows how close the relationships between the sequences are. The longer the branches of the tree the more evolutionary divergent the sequences are. 2GNX A is the original protein being investigated and was a mouse protein. The branches with marked with * indicate that this branch arrangement occured more then 75% of the time.|none]]<BR> | |||
==Structural analysis== | ==Structural analysis== | ||
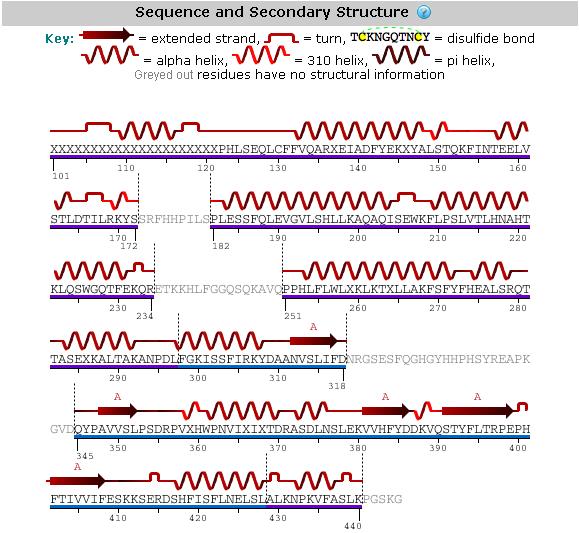
An analysis of the secondary structure of the protein from its amino acid sequence (Figure 3) shows the secondary structural arrangement of different regions of our protein | |||
[[Image:Mel's_picture_of_secondary_str..jpg|framed|'''Figure 3'''<BR>Secondary structure analysis of the 2GNX protein from Protein Data Bank.|none]]<BR> | |||
'''Table 1 ''' Dali analysis of the 2GNX protein | |||
NR. STRID1 STRID2 Z RMSD LALI LSEQ2 %IDE REVERS PERMUT NFRAG TOPO PROTEIN | NR. STRID1 STRID2 Z RMSD LALI LSEQ2 %IDE REVERS PERMUT NFRAG TOPO PROTEIN | ||
1: 3023-A 2gnx-A 42.9 0.0 280 280 100 0 0 1 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro | 1: 3023-A 2gnx-A 42.9 0.0 280 280 100 0 0 1 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro | ||
| Line 23: | Line 31: | ||
A Dali analysis (Table 1) of the 2GNX protein was highly inconclusive and there were no significant structural matches to the hypothetical protein. | A Dali analysis (Table 1) of the 2GNX protein was highly inconclusive and there were no significant structural matches to the hypothetical protein. | ||
'''Table 2 ''' Dali analysis of N-terminal domain | |||
NR. STRID1 STRID2 Z RMSD LALI LSEQ2 %IDE REVERS PERMUT NFRAG TOPO PROTEIN | NR. STRID1 STRID2 Z RMSD LALI LSEQ2 %IDE REVERS PERMUT NFRAG TOPO PROTEIN | ||
1: 3256-A 2gnx-A 23.2 0.0 173 280 100 0 0 1 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro | 1: 3256-A 2gnx-A 23.2 0.0 173 280 100 0 0 1 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro | ||
| Line 43: | Line 51: | ||
A Dali analysis carried out separately with only the N-terminal domain (Table 2) of the protein also did not produce any significant structural matches. | A Dali analysis carried out separately with only the N-terminal domain (Table 2) of the protein also did not produce any significant structural matches. | ||
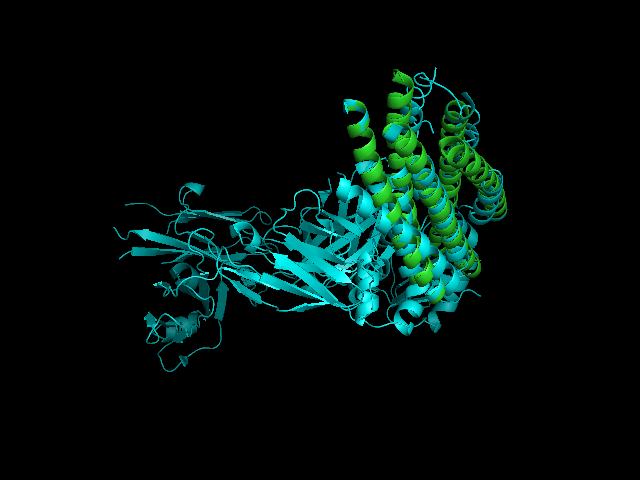
[[Image:2CMR 2GNX.png|framed|'''Figure 4'''<BR>2CMR-2GNX alignment (2CMR displayed in cyans and 2GNX displayed in green).|none]]<BR> | |||
A CE alignment between IMMUNOGLOBULIN COMPLEX d5 (2CMR) and 2GNX was performed (Figure 4). The result revealed that the N-terminus of 2GNX matched 2CMR:A which was a TRANSMEMBRANE GLYCOPROTEIN, with Rmsd = 3.8Å and Z-Score = 3.7. The 3D figure showed that two proteins both had five-helix strucuture and they were well fitted. However, the function of this 5-helix stucture was not clear. | |||
'''Table 3: Dali analysis of C-terminal domain''' | |||
NR. STRID1 STRID2 Z RMSD LALI LSEQ2 %IDE REVERS PERMUT NFRAG TOPO PROTEIN | NR. STRID1 STRID2 Z RMSD LALI LSEQ2 %IDE REVERS PERMUT NFRAG TOPO PROTEIN | ||
1: 3257-A 2gnx-A 24.3 0.0 118 280 100 0 0 1 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro | 1: 3257-A 2gnx-A 24.3 0.0 118 280 100 0 0 1 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro | ||
| Line 72: | Line 75: | ||
However, a Dali analysis (Table 3) carried out with the C-terminal domain of the protein produced one significant structural match, this being the GAF signalling protein, i.e the 4th result in the Dali analysis. | However, a Dali analysis (Table 3) carried out with the C-terminal domain of the protein produced one significant structural match, this being the GAF signalling protein, i.e the 4th result in the Dali analysis. | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Image-Dotlet.PNG|framed|'''Figure 5'''<BR>Dotlet analysis for 2GNX.|none]]<BR> | ||
The Dotlet analysis (Figure 5) showed that there was no internally homologous repeats in the C-terminus of 2GNX. | |||
The Dotlet analysis (Figure | |||
| Line 93: | Line 90: | ||
USR2:A 316/418 SHFISFLNELSLALKN | USR2:A 316/418 SHFISFLNELSLALKN | ||
Figure 6: CE predicted structural alignment. USR1 = 1MC0(PDB code), Regulatory Segment of Mouse 3',5'-Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase 2A, Containing the GAF A and GAF B Domains. USR2= 2GNX | |||
The conserved residues of the ligand binding site in 1MC0 were not consistent with the aligned residues in 2GNX. | The conserved residues of the ligand binding site in 1MC0 were not consistent with the aligned residues in 2GNX. | ||
| Line 101: | Line 100: | ||
SX(13-18)FDX(18-22)IAX(21)[Y/N]X(2)VDX(2)TX(3)TX(19)[E/Q] | SX(13-18)FDX(18-22)IAX(21)[Y/N]X(2)VDX(2)TX(3)TX(19)[E/Q] | ||
>2GNX | [[Image:Alignment.PNG|framed|'''Figure 7'''<BR>Fingerprint of the ligand binding site in 1MC0 (Zoraghi et al).The identical residues were coloured in red and the underline residues were the ones that missing in the PDB file. | ||
|none]]<BR> | |||
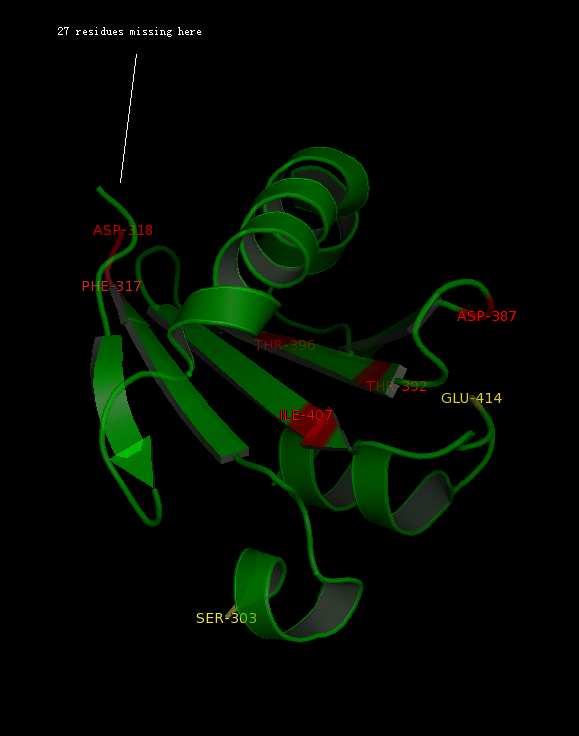
The alignment above (Figure 7) indicated that the published patterns roughly fit into the protein sequence of 2GNX. The 3D structure analysis (figure ) revealed that some residues (in yellow) were likely not within the ligand binding pocket, however other residues (in red) were still potential ligand binding site. | |||
[[Image:Ligand Qsite.png|framed|'''Figure 7.1'''<BR>Ligand Binding Site Predicted by Q-siteFinder | |||
|none]]<BR> | |||
The result from Q-siteFinder confirmed that there were probably protein binding pocket in the predicted region. However, the volume of the two pockets were small compare to a normal cGMP binding site (Zoraghi R, 2003). | |||
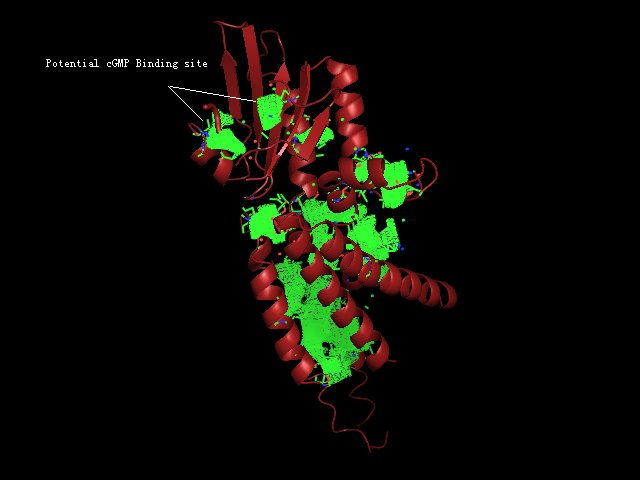
[[Image:Binding pocket.png|framed|'''Figure 8'''<BR> Potential ligand binding sites in 2GNX.|none]]<BR> | |||
The figure above | The figure above (Figure 8) shows the residues that are identical to the published patterns. The residues in red are the potential ligand binding residues and the residues in yellow were the residues that matched the published data but are not likely to be in the ligand binding pocket in 2GNX. | ||
== Functional Analysis == | == Functional Analysis == | ||
STRING and CDART returned no results for the submitted protein data. | STRING and CDART returned no results for the submitted protein data. | ||
=== | === BlastP Results === | ||
BlastP returned results however the results were limited to hypothetical proteins that gave no added information. | BlastP returned results however the results were limited to hypothetical proteins that gave no added information. | ||
'''Table 4:''' BlastP Results | |||
{| border="1" | {| border="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 310: | Line 311: | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== | === Method Predicted Subcellular Location Evaluation === | ||
Locate analysis predicted that the protein is a soluble non-secreted protein. Localisation data was diverse as follows: | Locate analysis predicted that the protein is a soluble non-secreted protein. Localisation data was diverse as follows: | ||
'''Table 5:''' Method Predicted Subcellular Location Evaluation | |||
{|border="1" | {|border="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 360: | Line 363: | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== | === BC048403 Symatlas Expression Profile === | ||
Pfam, Profunc, Proknow, and Interpro all returned no results for the protein 2gnxA. However, Symatlas did provide an interesting lead. The expression data is presented in the following diagram. However, the significant results were the number of olfactory receptors with correlated expression profiles. | Pfam, Profunc, Proknow, and Interpro all returned no results for the protein 2gnxA. However, Symatlas did provide an interesting lead. The expression data is presented in the following diagram. However, the significant results were the number of olfactory receptors with correlated expression profiles. | ||
[[Image:Symatlas bc048403 1.GIF]] | [[Image:Symatlas bc048403 1.GIF|framed|'''Figure 9'''<BR> Symatlas Expression Profile.<BR>|none]] | ||
=== | ===Co-occurring Motifs Corresponding to BC048403 === | ||
Olfactory receptors were also encountered when the protein was submitted to cis-RED to retrieve the corresponding cis-regulatory motif patterns. All fourteen motif patterns or modules, corresponding to the BC048403 protein are also motif patterns that are found in many different olfactory receptors. Motifs are predicted by cisRED with p-values < 0.005. | Olfactory receptors were also encountered when the protein was submitted to cis-RED to retrieve the corresponding cis-regulatory motif patterns. All fourteen motif patterns or modules, corresponding to the BC048403 protein are also motif patterns that are found in many different olfactory receptors. Motifs are predicted by cisRED with p-values < 0.005. | ||
In total, the fourteen motifs corresponded to 120 different olfactory receptors. The following table lists the olfactory receptors with 3 or more co-occurring motifs. The header row lists the fourteen modules. Highlighted in orange (nine co-occurring modules) and green (7 co-occurring modules), are the olfactory receptors having the most modules in common with the BC048403 protein. | In total, the fourteen motifs corresponded to 120 different olfactory receptors. The following table lists the olfactory receptors with 3 or more co-occurring motifs. The header row lists the fourteen modules. Highlighted in orange (nine co-occurring modules) and green (7 co-occurring modules), are the olfactory receptors having the most modules in common with the BC048403 protein. | ||
'''Table 6:''' Co-occurring Motifs Corresponding to Olfactory Receptors | |||
[[Image:Olf motif table.GIF]] | [[Image:Olf motif table.GIF]] | ||
=== | === Number of Motifs Corresponding to each Olfactory Receptor === | ||
The following graph represents the number of co-occurring motifs across the entire range of 120 corresponding olfactory receptors. | The following graph represents the number of co-occurring motifs across the entire range of 120 corresponding olfactory receptors. | ||
[[Image:Olf motif graph.GIF]] | [[Image:Olf motif graph.GIF |framed|'''Figure 10'''<BR> Graph of the number of motifs corresponding to each olfactory receptor.<BR>|none]] | ||
These motifs were searched for in the other species databases of cis-RED however they were not found as there is no inter-species search tool. Unfortunately, micro-array expression data for the olfactory receptors with the most co-occurring motifs, were unavailable. | These motifs were searched for in the other species databases of cis-RED however they were not found as there is no inter-species search tool. Unfortunately, micro-array expression data for the olfactory receptors with the most co-occurring motifs, were unavailable. | ||
=== | === Micro-array Expression Profiles Similar to FLJ32549 === | ||
The following micro-array data was found by browsing through the profile neighbours of the human ortholog using GEO Profiles. | The following micro-array data was found by browsing through the profile neighbours of the human ortholog using GEO Profiles. | ||
[[Image:Flj32549 expression profiles.GIF]] | [[Image:Flj32549 expression profiles.GIF|framed|'''Figure 11'''<BR> Neighbouring expression profiles to FLJ32549.|none]] | ||
Other interesting motifs found to appear in the Bc048403 protein were motifs that corresponded to the cadherin family. | Other interesting motifs found to appear in the Bc048403 protein were motifs that corresponded to the cadherin family. | ||
==Return to [[report]]== | ==Return to [[report]]== | ||
Latest revision as of 03:14, 12 June 2007
Evolutionary analysis
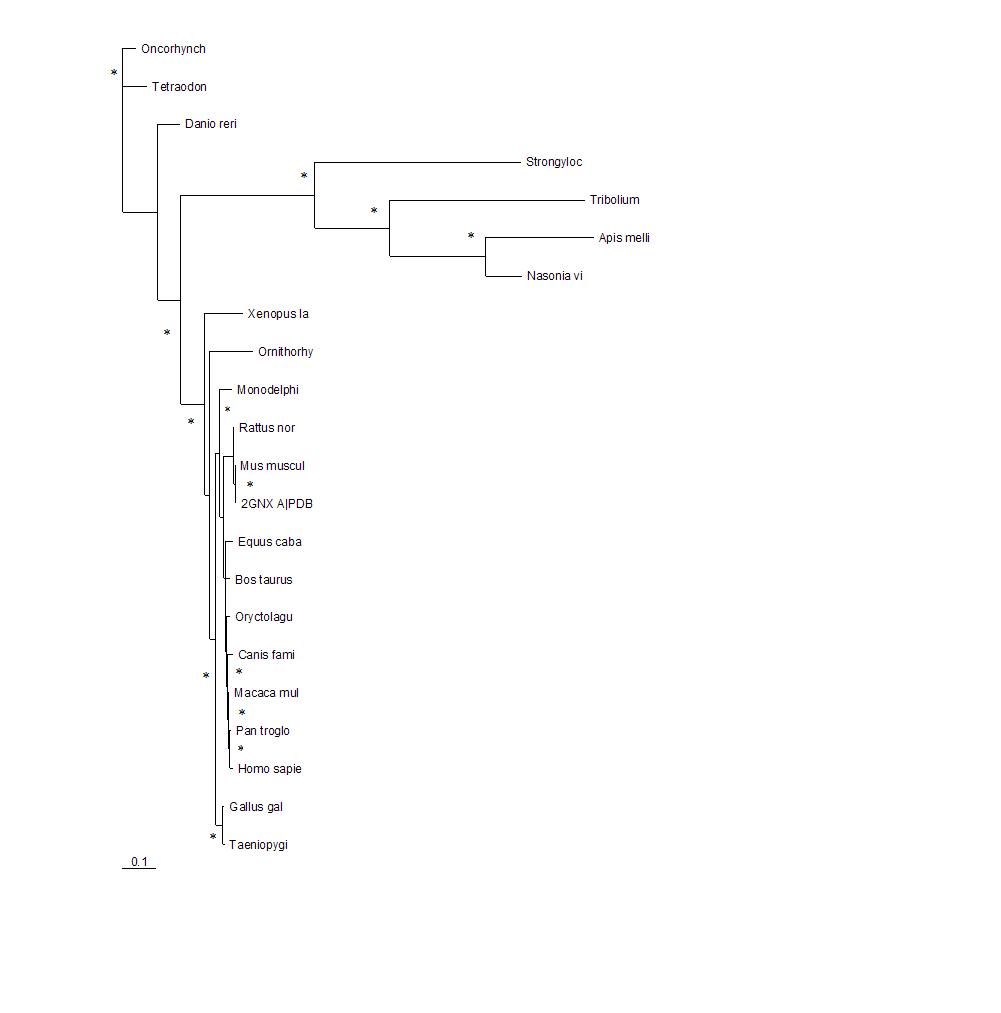
The phylogenetic tree shows how close the relationships between the sequences are. The longer the branches of the tree the more evolutionary divergent the sequences are. 2GNX A is the original protein being investigated and was a mouse protein. The branches with marked with * indicate that this branch arrangement occured more then 75% of the time.
Structural analysis
An analysis of the secondary structure of the protein from its amino acid sequence (Figure 3) shows the secondary structural arrangement of different regions of our protein
Table 1 Dali analysis of the 2GNX protein
NR. STRID1 STRID2 Z RMSD LALI LSEQ2 %IDE REVERS PERMUT NFRAG TOPO PROTEIN 1: 3023-A 2gnx-A 42.9 0.0 280 280 100 0 0 1 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro 2: 3023-A 2cmr-A 5.7 3.5 114 192 11 0 0 11 S IMMUNOGLOBULIN COMPLEX d5 (fab heavy chain) d5 (fab li 3: 3023-A 1j3w-A 5.7 3.2 99 134 12 0 0 9 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION giding protein-m 4: 3023-A 1jmr-A 5.5 3.0 94 246 9 0 0 12 S 5: 3023-A 1f5m-B 5.5 5.0 107 177 9 0 0 13 S SIGNALING PROTEIN gaf (saccharomyces cerevisiae) yeas 6: 3023-A 1vcs-A 5.0 4.7 82 102 9 0 0 8 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION vesicle transpor 7: 3023-A 1kt0-A 4.9 2.8 81 357 6 0 0 7 S ISOMERASE 51 kda fk506-binding protein (fkbp51) Mutant 8: 3023-A 1e2a-A 4.9 4.5 80 102 9 0 0 6 S TRANSFERASE enzyme iia (enzyme iii, lactose-specific i 9: 3023-A 2d2s-A 4.8 3.1 75 217 11 0 0 5 S ENDOCYTOSIS/EXOCYTOSIS exocyst complex component exo84 10: 3023-A 2oew-A 4.7 2.8 119 358 8 0 0 12 S PROTEIN TRANSPORT programmed cell death 6-interacting 11: 3023-A 1h3q-A 4.7 4.2 92 140 4 0 0 11 S TRANSPORT sedlin (sedl) (mus musculus) mouse S.B.Jan 12: 3023-A 2oev-A 4.5 36.5 151 697 7 0 0 14 S PROTEIN TRANSPORT programmed cell death 6-interacting 13: 3023-A 2cwy-A 4.5 2.4 82 92 20 0 0 7 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro 14: 3023-A 2c5i-T 4.5 2.8 75 93 11 0 0 5 S PROTEIN TRANSPORT/COMPLEX t-snare affecting a late gol 15: 3023-A 3nul 4.4 3.4 93 130 5 0 0 11 S ACTIN-BINDING PROTEIN profilin i (arabidopsis thalian
A Dali analysis (Table 1) of the 2GNX protein was highly inconclusive and there were no significant structural matches to the hypothetical protein.
Table 2 Dali analysis of N-terminal domain
NR. STRID1 STRID2 Z RMSD LALI LSEQ2 %IDE REVERS PERMUT NFRAG TOPO PROTEIN 1: 3256-A 2gnx-A 23.2 0.0 173 280 100 0 0 1 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro 2: 3256-A 1e2a-A 7.5 4.5 80 102 9 0 0 6 S TRANSFERASE enzyme iia (enzyme iii, lactose-specific i 3: 3256-A 1kt0-A 7.4 2.8 81 357 6 0 0 7 S ISOMERASE 51 kda fk506-binding protein (fkbp51) Mutant 4: 3256-A 2d2s-A 7.3 3.1 75 217 11 0 0 5 S ENDOCYTOSIS/EXOCYTOSIS exocyst complex component exo84 5: 3256-A 1vcs-A 7.3 4.7 78 102 9 0 0 7 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION vesicle transpor 6: 3256-A 2cmr-A 6.9 3.2 104 192 11 0 0 9 S IMMUNOGLOBULIN COMPLEX d5 (fab heavy chain) d5 (fab li 7: 3256-A 2c5i-T 6.9 2.8 75 93 11 0 0 5 S PROTEIN TRANSPORT/COMPLEX t-snare affecting a late gol 8: 3256-A 2h7o-A 6.8 3.0 81 270 5 0 0 7 S SIGNALING PROTEIN protein kinase ypka fragment (protei 9: 3256-A 2h7v-C 6.6 4.2 76 269 13 0 0 5 S SIGNALING PROTEIN migration-inducing protein 5 (ras-re 10: 3256-A 2dnx-A 6.5 4.9 80 130 6 0 0 6 S TRANSPORT PROTEIN syntaxin-12 fragment (homo sapiens) 11: 3256-A 1hg5-A 6.5 3.2 85 263 9 0 0 6 S ENDOCYTOSIS clathrin assembly protein short form frag 12: 3256-A 1a17 6.4 2.5 71 159 3 0 0 5 S HYDROLASE serineTHREONINE PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE 5 fragme 13: 3256-A 2if4-A 6.3 2.5 82 258 7 0 0 7 S SIGNALING PROTEIN atfkbp42 fragment (twd1 (twisted dwa 14: 3256-A 1owa-A 6.2 3.3 76 156 12 0 0 6 S CYTOKINE spectrin alpha chain, erythrocyte fragment (e 15: 3256-A 2oew-A 6.1 2.8 119 358 8 0 0 12 S PROTEIN TRANSPORT programmed cell death 6-interacting
A Dali analysis carried out separately with only the N-terminal domain (Table 2) of the protein also did not produce any significant structural matches.
A CE alignment between IMMUNOGLOBULIN COMPLEX d5 (2CMR) and 2GNX was performed (Figure 4). The result revealed that the N-terminus of 2GNX matched 2CMR:A which was a TRANSMEMBRANE GLYCOPROTEIN, with Rmsd = 3.8Å and Z-Score = 3.7. The 3D figure showed that two proteins both had five-helix strucuture and they were well fitted. However, the function of this 5-helix stucture was not clear.
Table 3: Dali analysis of C-terminal domain
NR. STRID1 STRID2 Z RMSD LALI LSEQ2 %IDE REVERS PERMUT NFRAG TOPO PROTEIN 1: 3257-A 2gnx-A 24.3 0.0 118 280 100 0 0 1 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro 2: 3257-A 1jmr-A 7.6 3.0 94 246 9 0 0 12 S 3: 3257-A 1j3w-A 7.5 2.9 91 134 13 0 0 7 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION giding protein-m 4: 3257-A 1f5m-B 6.8 2.9 95 177 9 0 0 10 S SIGNALING PROTEIN gaf (saccharomyces cerevisiae) yeas 5: 3257-A 1h3q-A 6.6 4.2 92 140 4 0 0 11 S TRANSPORT sedlin (sedl) (mus musculus) mouse S.B.Jan 6: 3257-A 3nul 6.3 3.4 93 130 5 0 0 11 S ACTIN-BINDING PROTEIN profilin i (arabidopsis thalian 7: 3257-A 1mc0-A 5.8 4.1 99 341 8 0 0 11 S HYDROLASE 3',5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 2a 8: 3257-A 2h28-A 5.4 2.8 75 106 8 0 0 10 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro 9: 3257-A 2p7j-A 5.0 2.9 79 262 13 0 0 11 S TRANSCRIPTION putative sensory boxGGDEF FAMILY PROTEIN 10: 3257-A 2dmw-A 5.0 3.3 85 131 7 0 0 11 S MEMBRANE PROTEIN synaptobrevin-like 1 variant fragment 11: 3257-A 2avx-A 4.8 3.6 93 171 5 0 0 10 S TRANSCRIPTION regulatory protein sdia Mutant (escheri 12: 3257-A 2j3t-C 4.7 5.2 83 141 7 0 0 8 S PROTEIN TRANSPORT trafficking protein particle complex 13: 3257-A 2hj9-C 4.7 3.3 76 210 5 0 0 9 S SIGNALING PROTEIN autoinducer 2-binding periplasmic pr 14: 3257-A 2hje-A 4.6 3.0 75 210 5 0 0 9 S SIGNALING PROTEIN autoinducer 2 sensor kinasePHOSPHATA 15: 3257-A 2uv0-E 4.5 3.5 93 159 9 0 0 12 S TRANSCRIPTION transcriptional activator protein lasr
However, a Dali analysis (Table 3) carried out with the C-terminal domain of the protein produced one significant structural match, this being the GAF signalling protein, i.e the 4th result in the Dali analysis.
The Dotlet analysis (Figure 5) showed that there was no internally homologous repeats in the C-terminus of 2GNX.
USR1:A 185/392 QVAKNLFTH---LDDVSVLLQEIITEARNLSNAEICSVFLLDQ----------------- USR2:A 181/283 TASEXKALTAKANPDLFGKISSFIRKY------DAANVSLIFDNRGSESFQGHGYHHPHS USR1:A 225/432 ----------NELVAKVFDGGVVDDESYEIRIPADQGIAGHVATTG----------QILN USR2:A 235/#44 YREAPKGVDQYPAVVSLP----------SDRPVXHWPNVIXIXTDRASDLNSLEKVVHFY USR1:A 265/472 IPDAYAHPLFYRGVDDSTGFRTRNILCFPIKNENQEVIGVAELVNKINGPWFSKFDEDLA USR2:A 285/387 DDKV-------------------QSTYFLTRPEP-HFTIVVIFESK---------KSERD USR1:A 325/532 TAFSIYCGISIAHSLL USR2:A 316/418 SHFISFLNELSLALKN
Figure 6: CE predicted structural alignment. USR1 = 1MC0(PDB code), Regulatory Segment of Mouse 3',5'-Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase 2A, Containing the GAF A and GAF B Domains. USR2= 2GNX
The conserved residues of the ligand binding site in 1MC0 were not consistent with the aligned residues in 2GNX.
Zoraghi R. et al. (2003) indicated a fingerprint of the ligand binding site in 1MC0, which was the following patterns:
SX(13-18)FDX(18-22)IAX(21)[Y/N]X(2)VDX(2)TX(3)TX(19)[E/Q]
The alignment above (Figure 7) indicated that the published patterns roughly fit into the protein sequence of 2GNX. The 3D structure analysis (figure ) revealed that some residues (in yellow) were likely not within the ligand binding pocket, however other residues (in red) were still potential ligand binding site.
The result from Q-siteFinder confirmed that there were probably protein binding pocket in the predicted region. However, the volume of the two pockets were small compare to a normal cGMP binding site (Zoraghi R, 2003).
The figure above (Figure 8) shows the residues that are identical to the published patterns. The residues in red are the potential ligand binding residues and the residues in yellow were the residues that matched the published data but are not likely to be in the ligand binding pocket in 2GNX.
Functional Analysis
STRING and CDART returned no results for the submitted protein data.
BlastP Results
BlastP returned results however the results were limited to hypothetical proteins that gave no added information.
Table 4: BlastP Results
| Score (Bits) | E Value | |||
| ref | XP_001163972.1 | PREDICTED: similar to FLJ32549 protein [Pan | 850 | 0.0 |
| ref | XP_001116860.1 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein isoform 1 [M | 848 | 0.0 |
| ref | NP_689653.3 | hypothetical protein LOC144577 [Homo sapiens... | 847 | 0.0 |
| gb | AAH36246.1 | FLJ32549 protein [Homo sapiens] | 846 | 0.0 |
| ref | XP_001116875.1 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein isoform 3 [M | 843 | 0.0 |
| ref | XP_531657.2 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein XP_531657 [Cani | 827 | 0.0 |
| ref | XP_615557.3 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein [Bos taurus] | 823 | 0.0 |
| gb | EDL24424.1 | cDNA sequence BC048403, isoform CRA_a [Mus muscul | 803 | 0.0 |
| ref | NP_766610.2 | hypothetical protein LOC270802 [Mus musculus... | 803 | 0.0 |
| ref | XP_576234.2 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein [Rattus norv... | 802 | 0.0 |
| ref | XP_001364942.1 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein [Monodelphis | 797 | 0.0 |
| ref | XP_416063.1 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein [Gallus gallus] | 796 | 0.0 |
| dbj | BAC39804.1 | unnamed protein product [Mus musculus] | 760 | 0.0 |
| ref | XP_001116868.1 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein isoform 2 [M | 743 | 0.0 |
| ref | NP_001085035.1 | hypothetical protein LOC432102 [Xenopus l... | 697 | 0.0 |
| ref | NP_001025261.1 | hypothetical protein LOC555715 [Danio rer... | 665 | 0.0 |
| ref | NP_001076454.1 | hypothetical protein LOC100005809 [Danio ... | 661 | 0.0 |
| ref | XP_001331282.1 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein [Danio rerio | 598 | 2e-169 |
| emb | CAG12393.1 | unnamed protein product [Tetraodon nigroviridis] | 593 | 8e-168 |
| pdb | 2GNX | A Chain A, X-Ray Structure Of A Hypothetical Protein... | 554 | 3e-156 |
| dbj | BAE41440.1 | unnamed protein product [Mus musculus] | 508 | 2e-142 |
| ref | NP_001038719.1 | hypothetical protein LOC692281 [Danio rer... | 357 | 1e-96 |
| ref | XP_624797.1 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein [Apis mellifera | 235 | 3e-60 |
| ref | XP_974676.1 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein [Tribolium cast | 232 | 5e-59 |
| ref | XP_001193974.1 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein [Strongyloce | 208 | 5e-52 |
| ref | XP_797380.2 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein, partial [St... | 207 | 2e-51 |
| dbj | BAE37112.1 | unnamed protein product [Mus musculus] >dbj B... | 134 | 2e-29 |
| gb | EDL24425.1 | cDNA sequence BC048403, isoform CRA_b [Mus muscul | 132 | 6e-29 |
| ref | XP_642387.1 | hypothetical protein DDBDRAFT_0205477 [Dicty... | 87.8 | 1e-15 |
| emb | CAJ08583.1 | hypothetical protein, conserved [Leishmania majo | 36.6 | 3.5 |
Method Predicted Subcellular Location Evaluation
Locate analysis predicted that the protein is a soluble non-secreted protein. Localisation data was diverse as follows:
Table 5: Method Predicted Subcellular Location Evaluation
| Method | Location | Score |
| CELLO | Mitochondrion | 1.34 |
| CELLO | Extracellular region | 1.08 |
| pTarget | Endoplasmic reticulum | 93.90 |
| Proteome Analyst | No prediction | 0.00 |
| WoLFPSORT | Cytoplasm | 13.00 |
| WoLFPSORT | Nucleus | 12.00 |
| WoLFPSORT | Golgi apparatus | 3.00 |
| MultiLoc | Peroxisome | 0.49 |
| MultiLoc | Mitochondrion | 0.23 |
| MultiLoc | Extracellular region | 0.09 |
BC048403 Symatlas Expression Profile
Pfam, Profunc, Proknow, and Interpro all returned no results for the protein 2gnxA. However, Symatlas did provide an interesting lead. The expression data is presented in the following diagram. However, the significant results were the number of olfactory receptors with correlated expression profiles.
Co-occurring Motifs Corresponding to BC048403
Olfactory receptors were also encountered when the protein was submitted to cis-RED to retrieve the corresponding cis-regulatory motif patterns. All fourteen motif patterns or modules, corresponding to the BC048403 protein are also motif patterns that are found in many different olfactory receptors. Motifs are predicted by cisRED with p-values < 0.005.
In total, the fourteen motifs corresponded to 120 different olfactory receptors. The following table lists the olfactory receptors with 3 or more co-occurring motifs. The header row lists the fourteen modules. Highlighted in orange (nine co-occurring modules) and green (7 co-occurring modules), are the olfactory receptors having the most modules in common with the BC048403 protein.
Table 6: Co-occurring Motifs Corresponding to Olfactory Receptors
Number of Motifs Corresponding to each Olfactory Receptor
The following graph represents the number of co-occurring motifs across the entire range of 120 corresponding olfactory receptors.
These motifs were searched for in the other species databases of cis-RED however they were not found as there is no inter-species search tool. Unfortunately, micro-array expression data for the olfactory receptors with the most co-occurring motifs, were unavailable.
Micro-array Expression Profiles Similar to FLJ32549
The following micro-array data was found by browsing through the profile neighbours of the human ortholog using GEO Profiles.
Other interesting motifs found to appear in the Bc048403 protein were motifs that corresponded to the cadherin family.