Function: Difference between revisions
From MDWiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (51 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The predicted function based on the evolution and structure | |||
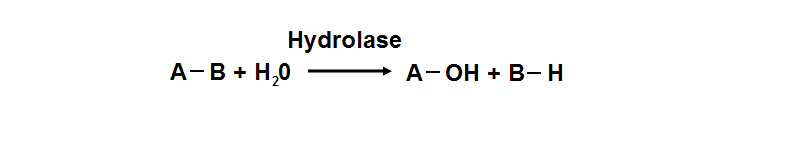
<font size = "4">'''Hydrolase'''</font> | |||
[[Image:Document18_01.png]] | |||
Hydrolyase catalyze the hydrosis of the chemical bond between A and B, resulting of 2 simple molecules | |||
* Hydrolase | |||
** Catalyze hydrolysis reaction | |||
** Addition of the hydrogen and hydroxyl ions of water | |||
** Splitting into 2 or more simpler molecules | |||
** EC class 3 | |||
== Function of sulfatases == | |||
Sulfatases are enzymes,which hydrolyse sulfate ester bonds of substrates. | |||
Most of the family members has shown to contain a highly conserved cystine residue and a bivalent metal binding site. | |||
== Functional site== | |||
MSA data revealed some conserved residues on the sequence. They were mapped on the three dimantional structure. | |||
[[Image:Zn_Cl_surface]] | |||
---- | |||
Click here to go [http://compbio.chemistry.uq.edu.au/mediawiki/index.php/BIOL3004_2007 ''Back''] | |||
Latest revision as of 09:44, 20 May 2008
The predicted function based on the evolution and structure
Hydrolase
Hydrolyase catalyze the hydrosis of the chemical bond between A and B, resulting of 2 simple molecules
- Hydrolase
- Catalyze hydrolysis reaction
- Addition of the hydrogen and hydroxyl ions of water
- Splitting into 2 or more simpler molecules
- EC class 3
Function of sulfatases
Sulfatases are enzymes,which hydrolyse sulfate ester bonds of substrates. Most of the family members has shown to contain a highly conserved cystine residue and a bivalent metal binding site.
Functional site
MSA data revealed some conserved residues on the sequence. They were mapped on the three dimantional structure.
Click here to go Back