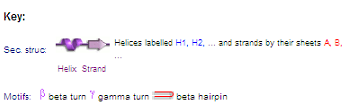Structure ERp18: Difference between revisions
John O'Bryen (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
John O'Bryen (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[http://compbio.chemistry.uq.edu.au/mediawiki/index.php/Endoplasmic_reticulum_thioredoxin_superfamily_member Back] | |||
== Methods == | == Methods == | ||
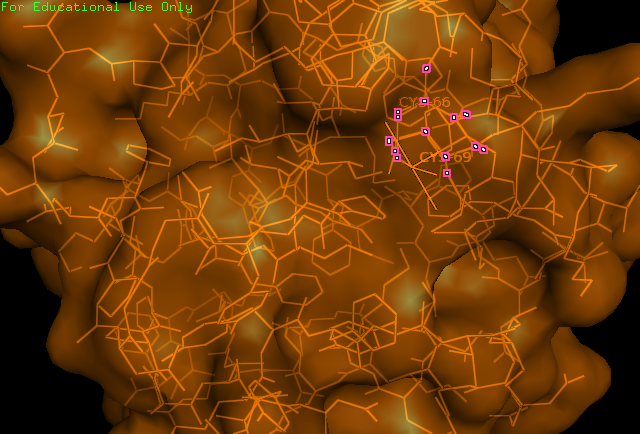
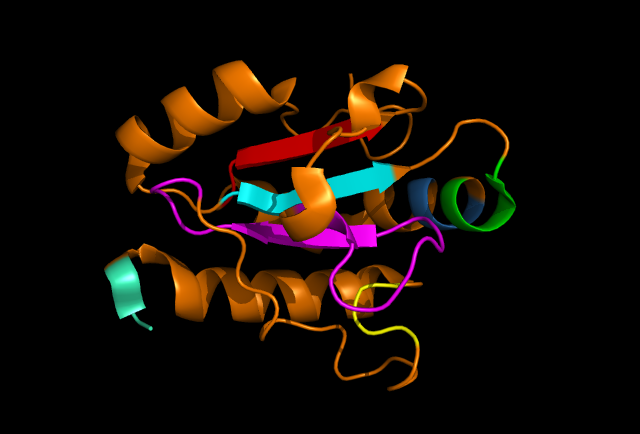
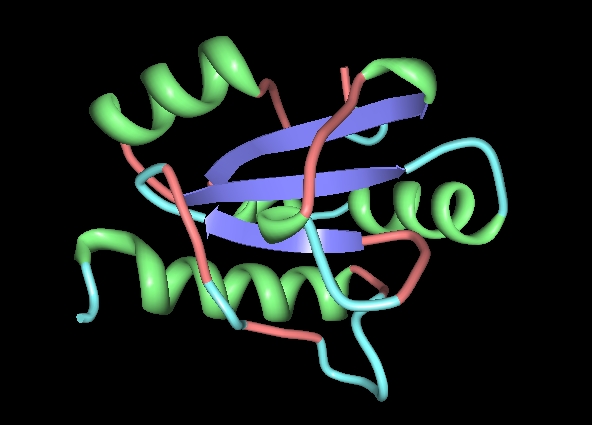
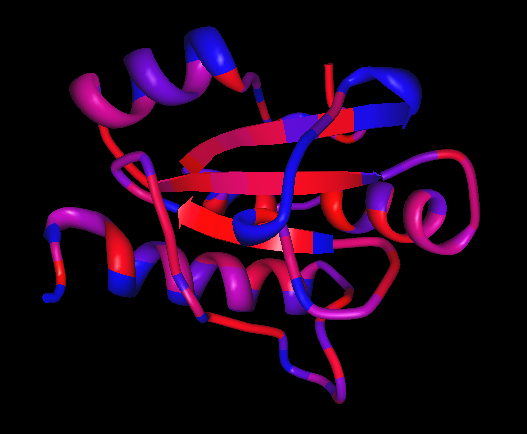
Study of the ERp18 protein (ID = 1sen-A) began by obtaining its file from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) and visualising the 3D structure of the protein using PyMOL. It was known from study about its function that ERp18 contains a CXXC motif[1], characteristic of all thiol-disulfide oxidoreductases - this motif was identified as residues <sup>66</sup>CGAC<sup>69</sup> of the amino acid sequence of mature ERp18. These catalytic cysteine residues were found to be localised to the surface of the protein and thus were predicted to form the catalytic site. Next, conserved sequences identified by a ClustalX multiple alignment from evolution study were highlighted on the protein. PDB ProteinWorkshop 3.4 was used to map conformation types and hydrophobicity of ERp18. Following this, searches were made with PDBsum, SCOP, and Prosite for more information about the folding and domain-annotation of the protein. A search with DALI revealed a list of structurally related proteins, from which a number of comparisons were made. Secondary structures of 1sen-A and other proteins identified via the DALI search were provided by PDBsum. After completing these fundamental protein structure searches, published papers were consulted and their findings on ERp18 were compared and integrated with our findings. | Study of the ERp18 protein (ID = 1sen-A) began by obtaining its file from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) and visualising the 3D structure of the protein using PyMOL. It was known from study about its function that ERp18 contains a CXXC motif[1], characteristic of all thiol-disulfide oxidoreductases - this motif was identified as residues <sup>66</sup>CGAC<sup>69</sup> of the amino acid sequence of mature ERp18. These catalytic cysteine residues were found to be localised to the surface of the protein and thus were predicted to form the catalytic site. Next, conserved sequences identified by a ClustalX multiple alignment from evolution study were highlighted on the protein. PDB ProteinWorkshop 3.4 was used to map conformation types and hydrophobicity of ERp18. Following this, searches were made with PDBsum, SCOP, and Prosite for more information about the folding and domain-annotation of the protein. A search with DALI revealed a list of structurally related proteins, from which a number of comparisons were made. Secondary structures of 1sen-A and other proteins identified via the DALI search were provided by PDBsum. After completing these fundamental protein structure searches, published papers were consulted and their findings on ERp18 were compared and integrated with our findings. | ||
| Line 5: | Line 7: | ||
[[Image: Image_of_CC_residues.png|framed|'''Figure 1:''' | [[Image: Image_of_CC_residues.png|framed|'''Figure 1:''' The catalytic cysteine residues (66,69) of ERp18. These residues fit the CXXC motif ubiquitous of all thiol–disulfide oxidoreductases. ''Image produced using PyMOL.''|none]]<BR> | ||
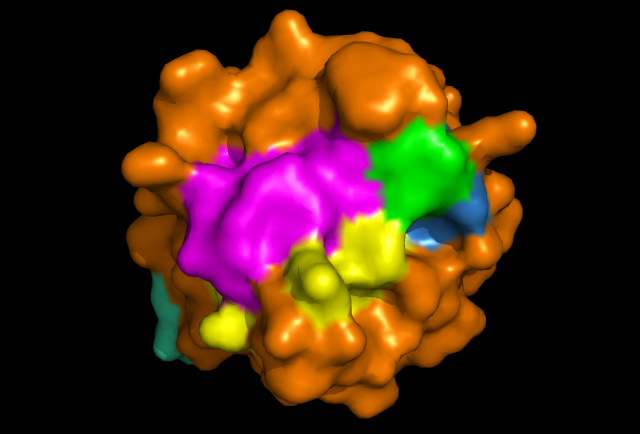
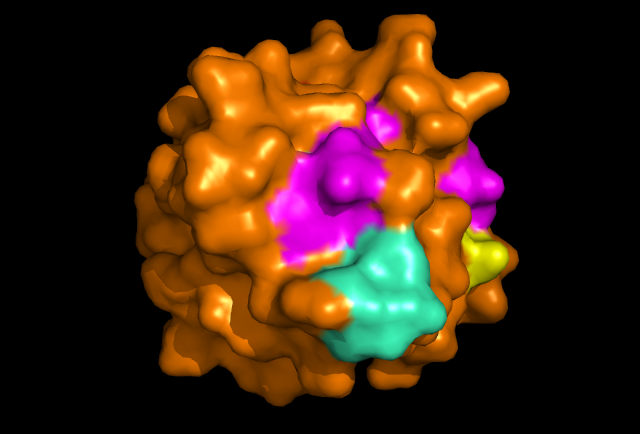
[[Image: Image_1.png|framed|'''Figure 2:''' Front view displaying highly conserved surface residues, which surround the location of the cysteine residues. These conserved surface residues are hypothesised to form the active site of ERp18. Conserved residues on this front view are shown in pink, green, yellow, and dark blue. These residues correspond to continuous segments of highly conserved amino acids. ''Image produced using PyMOL.''|none]]<BR> | |||
Pockets around the predicted catalytic site were identified as potential binding sites by Q-SiteFinder and CASTp, being in the top hits for these ligand binding site searches. | Pockets around the predicted catalytic site were identified as potential binding sites by Q-SiteFinder and CASTp, being in the top hits for these ligand binding site searches. | ||
[[Image: Image_2.png|framed|'''Figure 3:''' | |||
[[Image: Image_2.png|framed|'''Figure 3:''' Rear view displaying another area of conservation (shown as purple and light blue regions). This area is not believed to have any catalytic activity; nevertheless, it is likely to have some importance - perhaps as a targeting signal or as an area for association with another protein. ''Image produced using PyMOL.''|none]]<BR> | |||
[[Image: Ribbon_structure.png|framed|'''Figure 4:''' | [[Image: Ribbon_structure.png|framed|'''Figure 4:''' Highly conserved sections of a ribbon diagram of ERp18. Notice the conservation of the three core beta sheets - probably vital for maintaining stability and correct folding of the protein, as well as correct catalytic activity. ''Image produced using PyMOL.''|none]]<BR> | ||
| Line 26: | Line 30: | ||
2. Class: Alpha and beta proteins (a/b) [51349] | 2. Class: Alpha and beta proteins (a/b) [51349] | ||
Mainly parallel beta sheets (beta-alpha-beta units) | Mainly parallel beta sheets (beta-alpha-beta units) | ||
3. Fold: Thioredoxin fold [52832] | 3. Fold: '''Thioredoxin fold''' [52832] | ||
core: 3 layers, a/b/a; mixed beta-sheet of 4 strands, order 4312; strand 3 is antiparallel to the rest | core: 3 layers, a/b/a; mixed beta-sheet of 4 strands, order 4312; strand 3 is antiparallel to the rest | ||
4. Superfamily: Thioredoxin-like [52833] | 4. Superfamily: Thioredoxin-like [52833] | ||
| Line 32: | Line 36: | ||
6. Protein: Thioredoxin-like protein p19, TLP19 [110604] | 6. Protein: Thioredoxin-like protein p19, TLP19 [110604] | ||
7. Species: Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606] [110605] | 7. Species: Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606] [110605] | ||
'''Figure 5:''' SCOP summary of ERp18. The summary confirms the presence of a thioredoxin fold, hence its classification as a 'thioredoxin-like protein'. | |||
[[Image: Conformation_type_of_ERp18.png|framed|'''Figure | [[Image: Conformation_type_of_ERp18.png|framed|'''Figure 6:''' The conformation types making up ERp18. | ||
Turn = Light Blue, | Turn = Light Blue, | ||
| Line 44: | Line 50: | ||
Strand = Dark Blue | Strand = Dark Blue | ||
|none]]<BR> | ''Image produced using PDB ProteinWorkshop 3.4.''|none]]<BR> | ||
[[Image: Hydrophobicity_2.png|framed|'''Figure | [[Image: Hydrophobicity_2.png|framed|'''Figure 7:''' Hydrophobicity mapping of ERp18. Most hydrophobic = red, least hydrophobic = blue. ''Image produced using PDB ProteinWorkshop 3.4.''|none]]<BR> | ||
| Line 84: | Line 90: | ||
30: 2vlt-B 10.1 2.4 100 110 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN H ISOFORM 2.; | 30: 2vlt-B 10.1 2.4 100 110 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN H ISOFORM 2.; | ||
'''Figure | |||
'''Figure 8:''' The top thirty hits from a DALI search with 1sen-A. DALI lists proteins in order of their structural similarity. The protein names displayed are almost entirely thiol:disulfide interchange proteins and thioredoxins (thioredoxins being a related protein to the catalytic domain of thiol:disulfide interchange proteins), with the exception of 'putative exported cytochrome c biogenesis-related protein' for 2 and 3. However, hits 2 and 3 contain the CXXC motif and are therefore likely to be members of the thioredoxin family. Interestingly, the percent identification (%id) of these hits ranges between 12-23% - quite low considering the degree of structural homology as assigned by the rmsd value, for which structure similarity is considered significant if the value is less than approximately 3.5. | |||
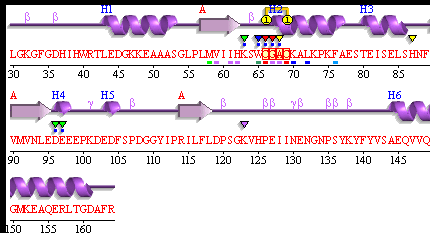
[[Image: Pdbsum_1senA.gif|framed|'''Figure 9:''' Secondary Structure of 1sen (ERp18). ''Image taken from PDBsum.''|none]]<BR> | |||
[[Image: Key_for_secondary_structure.png]] | |||
[[Image: Pdbsum_3fpu.gif|framed|'''Figure 10:''' Secondary Structure of 3f9u . ''Image taken from PDBsum.''|none]]<BR> | |||
| Line 99: | Line 112: | ||
UniProt: | UniProt: | ||
O95881 (TXD12_HUMAN) SAS | O95881 (TXD12_HUMAN) SAS | ||
Seq: 172 a.a. | |||
Struc: 135 a.a. | '''Seq: 172 a.a.''' | ||
'''Struc: 135 a.a.''' | |||
Key: PfamB domain | Key: PfamB domain | ||
Secondary structure CATH domain | Secondary structure CATH domain | ||
| Line 106: | Line 122: | ||
Enzyme class: E.C.1.8.4.2 [IntEnz] [ExPASy] [KEGG] [BRENDA] | Enzyme class: E.C.1.8.4.2 [IntEnz] [ExPASy] [KEGG] [BRENDA] | ||
Reaction: '''2 glutathione + protein-disulfide = glutathione disulfide + protein- dithiol''' | Reaction: '''2 glutathione + protein-disulfide = glutathione disulfide + protein- dithiol''' | ||
Resolution: 1.20Å | Resolution: 1.20Å | ||
| Line 125: | Line 141: | ||
'''Figure 11:''' PDBsum summary of ERp18. Importantly, it predicts the reaction catalysed by ERp18. | |||
== Discussion == | |||
Localisation of the CXXC motif to a highly conserved surface region indicated that it forms a putative active site. This was supported by bioinformatics programs such as Q-SiteFinder and CASTp which predicted ligand binding sites at the putative catalytic site. Other conserved areas such as the second surface region and the internal B-sheets are most likely indicative of their role in correct conformation and activity of the protein. The conformation type and hydrophobicity mapping of ERp18 provided by PDB ProteinWorkshop 3.4 supports the crystal structure conformation. The search results from SCOP, PDBsum, and Prosite identified ERp18 as a thioredoxin protein, which is consistent with the DALI search, which gave an output almost entirely of thioredoxins and thiol:disulfide interchange proteins. The literature identifies ERp18 as a homodimer, with a single protein having a molecular weight of 16.4 kDa[1]. Although the <sup>66</sup>CGAC<sup>69</sup> residues correspond to the CXXC motif of the thioredoxin superfamily, the <sup>66</sup>CGAC<sup>69</sup> residue sequence is unusual[2]. This, as well as ERp18's low identity to other proteins, makes ERp18 a novel member of the thioredoxin superfamily[2][3]. This structural analysis supports the function of ERp18 as a thioredoxin and provides grounds for further elucidation of ERp18's function and evolutionary history. | |||
[http://compbio.chemistry.uq.edu.au/mediawiki/index.php/Endoplasmic_reticulum_thioredoxin_superfamily_member Back] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 140: | Line 153: | ||
1. Jeong, W., Lee, D., Park, S., & Rhee, S.G., (2008) "ERp16, an Endoplasmic Reticulum-resident Thiol-disulfide Oxidoreductase" ''The Journal of Biological Chemistry'', Vol. 283, No. 37, pp. 25557–25566. | 1. Jeong, W., Lee, D., Park, S., & Rhee, S.G., (2008) "ERp16, an Endoplasmic Reticulum-resident Thiol-disulfide Oxidoreductase" ''The Journal of Biological Chemistry'', Vol. 283, No. 37, pp. 25557–25566. | ||
2. | 2. Alanen, H. I. et al. (2003) "Functional Characterization of ERp18, a New Endoplasmic Reticulum-located Thioredoxin Superfamily Member" ''The Journal of Biological Chemistry'', Vol. 278, No. 31, Issue of August 1, pp. 28912–28920. | ||
3. | 3. Liu, F., Rong, Y., Zeng, L., Zhang, X., & Han, Z.,(2003) "Isolation and characterization of a novel human thioredoxin-like gene hTLP19 encoding a secretory protein" ''Gene'', Volume:315, pp. 71–78. | ||
Latest revision as of 00:37, 16 June 2009
Methods
Study of the ERp18 protein (ID = 1sen-A) began by obtaining its file from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) and visualising the 3D structure of the protein using PyMOL. It was known from study about its function that ERp18 contains a CXXC motif[1], characteristic of all thiol-disulfide oxidoreductases - this motif was identified as residues 66CGAC69 of the amino acid sequence of mature ERp18. These catalytic cysteine residues were found to be localised to the surface of the protein and thus were predicted to form the catalytic site. Next, conserved sequences identified by a ClustalX multiple alignment from evolution study were highlighted on the protein. PDB ProteinWorkshop 3.4 was used to map conformation types and hydrophobicity of ERp18. Following this, searches were made with PDBsum, SCOP, and Prosite for more information about the folding and domain-annotation of the protein. A search with DALI revealed a list of structurally related proteins, from which a number of comparisons were made. Secondary structures of 1sen-A and other proteins identified via the DALI search were provided by PDBsum. After completing these fundamental protein structure searches, published papers were consulted and their findings on ERp18 were compared and integrated with our findings.
Results
Pockets around the predicted catalytic site were identified as potential binding sites by Q-SiteFinder and CASTp, being in the top hits for these ligand binding site searches.
SCOP Summary
Protein: Thioredoxin-like protein p19, TLP19 from Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606] Lineage:
1. Root: scop
2. Class: Alpha and beta proteins (a/b) [51349]
Mainly parallel beta sheets (beta-alpha-beta units)
3. Fold: Thioredoxin fold [52832]
core: 3 layers, a/b/a; mixed beta-sheet of 4 strands, order 4312; strand 3 is antiparallel to the rest
4. Superfamily: Thioredoxin-like [52833]
5. Family: Thioltransferase [52834]
6. Protein: Thioredoxin-like protein p19, TLP19 [110604]
7. Species: Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606] [110605]
Figure 5: SCOP summary of ERp18. The summary confirms the presence of a thioredoxin fold, hence its classification as a 'thioredoxin-like protein'.
Dali Summary
No: Chain Z rmsd lali nres %id PDB Description 1: 1sen-A 31.6 0.0 134 134 100 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN-LIKE PROTEIN P19; 2: 3f9u-A 13.0 2.2 114 145 12 PDB MOLECULE: PUTATIVE EXPORTED CYTOCHROME C BIOGENESIS- 3: 3f9u-B 12.3 2.2 114 148 12 PDB MOLECULE: PUTATIVE EXPORTED CYTOCHROME C BIOGENESIS- 4: 2fwe-A 11.7 2.4 107 122 21 PDB MOLECULE: THIOL:DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE PROTEIN DSBD; 5: 2fwf-A 11.6 2.4 107 123 21 PDB MOLECULE: THIOL:DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE PROTEIN DSBD; 6: 1se1-C 11.1 2.1 103 231 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOL:DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE PROTEIN DSBD; 7: 1vrs-F 11.1 2.1 103 118 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOL:DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE PROTEIN DSBD; 8: 1vrs-D 11.1 2.2 102 118 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOL:DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE PROTEIN DSBD; 9: 1se1-A 11.1 2.2 102 239 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOL:DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE PROTEIN DSBD; 10: 1ep7-B 10.9 2.4 102 112 13 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN CH1, H-TYPE; 11: 2fwg-A 10.9 2.7 106 122 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOL:DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE PROTEIN DSBD; 12: 2fwh-A 10.9 2.2 102 117 23 PDB MOLECULE: THIOL:DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE PROTEIN DSBD; 13: 1uc7-A 10.8 2.2 104 124 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOL:DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE PROTEIN DSBD; 14: 1ep8-B 10.8 2.5 103 112 13 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN CH1, H-TYPE; 15: 1ep8-A 10.7 2.5 103 112 13 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN CH1, H-TYPE; 16: 2ju5-A 10.6 2.2 105 144 17 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN DISULFIDE ISOMERASE; 17: 1ep7-A 10.6 2.6 103 112 13 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN CH1, H-TYPE; 18: 1vrs-E 10.6 2.2 102 118 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOL:DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE PROTEIN DSBD; 19: 1uc7-B 10.5 2.3 104 124 23 PDB MOLECULE: THIOL:DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE PROTEIN DSBD; 20: 3d22-A 10.4 2.8 108 129 13 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN H-TYPE; 21: 3d21-A 10.4 2.5 101 111 16 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN H-TYPE; 22: 3d21-B 10.3 2.5 101 111 16 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN H-TYPE; 23: 3fk8-A 10.2 2.6 106 131 17 PDB MOLECULE: DISULPHIDE ISOMERASE; 24: 2vlv-B 10.2 2.3 99 113 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN H ISOFORM 2.; 25: 1se1-B 10.2 2.2 102 243 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOL:DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE PROTEIN DSBD; 26: 2vlu-B 10.2 2.3 100 112 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN H ISOFORM 2.; 27: 2vm1-A 10.2 2.3 99 110 16 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN H ISOFORM 1.; 28: 2vlv-A 10.1 2.4 100 111 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN H ISOFORM 2.; 29: 2vm2-A 10.1 2.3 99 109 16 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN H ISOFORM 1.; 30: 2vlt-B 10.1 2.4 100 110 22 PDB MOLECULE: THIOREDOXIN H ISOFORM 2.;
Figure 8: The top thirty hits from a DALI search with 1sen-A. DALI lists proteins in order of their structural similarity. The protein names displayed are almost entirely thiol:disulfide interchange proteins and thioredoxins (thioredoxins being a related protein to the catalytic domain of thiol:disulfide interchange proteins), with the exception of 'putative exported cytochrome c biogenesis-related protein' for 2 and 3. However, hits 2 and 3 contain the CXXC motif and are therefore likely to be members of the thioredoxin family. Interestingly, the percent identification (%id) of these hits ranges between 12-23% - quite low considering the degree of structural homology as assigned by the rmsd value, for which structure similarity is considered significant if the value is less than approximately 3.5.
PDBsum
PDB id: 1sen Name: Structural genomics, unknown function Title: Endoplasmic reticulum protein rp19 o95881
Structure: Thioredoxin-like protein p19. Chain: a. Synonym: endoplasmic reticulum protein erp19. Engineered: yes
Source: Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: tlp19. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Other_details: the protein was cloned, expressed and purified by the secsg human protein production group (t.A. Dailey, m. Mayer) under the direction of h.A. Dailey.
UniProt: O95881 (TXD12_HUMAN) SAS
Seq: 172 a.a.
Struc: 135 a.a.
Key: PfamB domain Secondary structure CATH domain
Enzyme class: E.C.1.8.4.2 [IntEnz] [ExPASy] [KEGG] [BRENDA]
Reaction: 2 glutathione + protein-disulfide = glutathione disulfide + protein- dithiol
Resolution: 1.20Å
R-factor: 0.162
R-free: 0.183
Authors: Z.-J.Liu,L.Chen,W.Tempel,A.Shah,D.Lee,T.A.Dailey,M.R.Mayer, J.P.Rose,D.C.Richardson,J.S.Richardson,H.A.Dailey,B.-C.Wang Southeast Collaboratory For Structural Genomics (Secsg)
Key ref: z.-j.liu et al. Endoplasmic reticulum protein Rp19. To be Published, xsi:nil="true" />.
Date: 17-Feb-04
Release date: 13-Jul-04
Related entries: O95881 related db: targetdb
Figure 11: PDBsum summary of ERp18. Importantly, it predicts the reaction catalysed by ERp18.
Discussion
Localisation of the CXXC motif to a highly conserved surface region indicated that it forms a putative active site. This was supported by bioinformatics programs such as Q-SiteFinder and CASTp which predicted ligand binding sites at the putative catalytic site. Other conserved areas such as the second surface region and the internal B-sheets are most likely indicative of their role in correct conformation and activity of the protein. The conformation type and hydrophobicity mapping of ERp18 provided by PDB ProteinWorkshop 3.4 supports the crystal structure conformation. The search results from SCOP, PDBsum, and Prosite identified ERp18 as a thioredoxin protein, which is consistent with the DALI search, which gave an output almost entirely of thioredoxins and thiol:disulfide interchange proteins. The literature identifies ERp18 as a homodimer, with a single protein having a molecular weight of 16.4 kDa[1]. Although the 66CGAC69 residues correspond to the CXXC motif of the thioredoxin superfamily, the 66CGAC69 residue sequence is unusual[2]. This, as well as ERp18's low identity to other proteins, makes ERp18 a novel member of the thioredoxin superfamily[2][3]. This structural analysis supports the function of ERp18 as a thioredoxin and provides grounds for further elucidation of ERp18's function and evolutionary history.
References
1. Jeong, W., Lee, D., Park, S., & Rhee, S.G., (2008) "ERp16, an Endoplasmic Reticulum-resident Thiol-disulfide Oxidoreductase" The Journal of Biological Chemistry, Vol. 283, No. 37, pp. 25557–25566.
2. Alanen, H. I. et al. (2003) "Functional Characterization of ERp18, a New Endoplasmic Reticulum-located Thioredoxin Superfamily Member" The Journal of Biological Chemistry, Vol. 278, No. 31, Issue of August 1, pp. 28912–28920.
3. Liu, F., Rong, Y., Zeng, L., Zhang, X., & Han, Z.,(2003) "Isolation and characterization of a novel human thioredoxin-like gene hTLP19 encoding a secretory protein" Gene, Volume:315, pp. 71–78.