|
|
| Line 14: |
Line 14: |
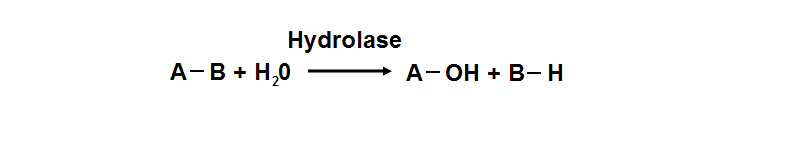
| ** Splitting into 2 or more simpler molecules | | ** Splitting into 2 or more simpler molecules |
| ** EC class 3 | | ** EC class 3 |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| <font size = "4">'''Gene Ontology'''</font>
| |
|
| |
| [[Image:Document17_01.png]]
| |
|
| |
| List of all matched protein name terms for 2gfh. The score in red is a measure of how strongly the term is predicted from the hits obtained by
| |
|
| |
| the different methods. The scores in blue show each method<nowiki>’</nowiki>s contribution to the total score (with the number of relevant
| |
|
| |
| sequences/structures shown in brackets in grey).(http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/)
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| * Higest score in GO - Hydrolase
| |
|
| |
| * Followed by - Phosphatase
| |
|
| |
| *Polymer: Haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain containing 4
| |
|
| |
| *Molecular Function: None
| |
|
| |
| *Biological Process: None
| |
|
| |
| *Cellular Component: None
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| <font size = "4">'''Surface Properties'''</font>
| |
|
| |
| [[Image:Document7_07.png]]
| |
| '''Figure 13. (A) '''Molecular structure of 2gfh with the ligand PO<sub>4.</sub>''' (B) '''Molecular and chemical structure of PO<sub>4.</sub>''' (C) '''Ligand interaction involving PO<sub>4.</sub> (Picture adapted from Profunc)
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| * Identify the likely biochemical function from the 3D structure
| |
|
| |
| * Possible binding sites and potential ligands - PO<sub>4</sub>
| |
|
| |
| * PO<sub>4</sub> most likely be an active site and fuction
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| <font size = "4">'''Phostphatase'''</font>
| |
|
| |
| [[Image:Document9_01.png]]
| |
|
| |
| MSA of the 2gfh with 35 others proteins. Only the 60<sup>th</sup> – 70<sup>th</sup> and the 210<sup>th</sup> -300<sup>th</sup> amino acid
| |
|
| |
| sequence were shown to illustrate the conserved and invariant regions. The 3 boxed-up sequences were either conserved or invariant regions.
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| * 1st - aspartic acid (D)
| |
|
| |
| * 2nd - threonine (T), asparagine (N) and glycine (G)
| |
|
| |
| * 3rd - lysine (K) and aspartates (D)
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| * MSA corelate with with study done by Maliekal et al
| |
| **N-acetylneuraminic acid phosphatase orthologs shared 3 motifs found in phosphatases
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| *HAD (Haloacid dehalogenase-like) family
| |
| ** Phosphatase activity: CO–P bond hydrolysis
| |
| ** Dehalogenase activity: C–halogen bond hydrolysis
| |
| ** Phosphonatase: C–P bond hydrolysis
| |
| ** Phosphoglucomutase: CO–P bond hydrolysis and intramolecular phosphoryl transfer
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| <font size = "4">'''Role in Human'''</font>
| |
|
| |
| * OMIM
| |
| ** Haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain
| |
| ** Gene map locus 20p11
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| [[Image:Document2_01.png]]
| |
|
| |
| Dephosphorylation of Neu5Ac-9-P is a reversible reaction with an end product of Neu5Ac (sialic acid) and a free phosphate.
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| * Main form of sialic acid in vertebrates
| |
| ** Important roles in protein-protein and cell-cell recognition
| |
| ** Dependent on the presence of Mg<sup>2+</sup>
| |
| ** Inhibited by vanadate and Ca<sup>2+</sup>
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| <font size = "4">'''Role in Bacteria - ''E.coli'''''</font>
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| * Hydrolyze a wide range of phosphorylated metabolites
| |
| ** Carbohydrates
| |
| ** Nucleotides,
| |
| ** Organic acids
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| * Kuznetsova ''et al'' - glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathway
| |
| ** Fructose-1-phosphate
| |
| ** Glucose-6-phosphate
| |
| ** Mannose-6-phosphate
| |
| ** 2-deoxyglucose-6-phosphate
| |
| ** Fructose-6- phosphate
| |
| ** Ribose-5-phosphate
| |
| ** Erythrose- 4-phosphate
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| [[Image:Document20_01.png]]
| |
|
| |
| [[Image:Document20_02.png]]
| |
|
| |
| Schematic diagrams of glycolysis and pentose phosphate metabolic pathways. The green arrows show the substrates that are hydrolyzed by HADs (http://www.steve.gb.com/science/core_metabolism.html)
| |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|