Results - 2gqnA: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
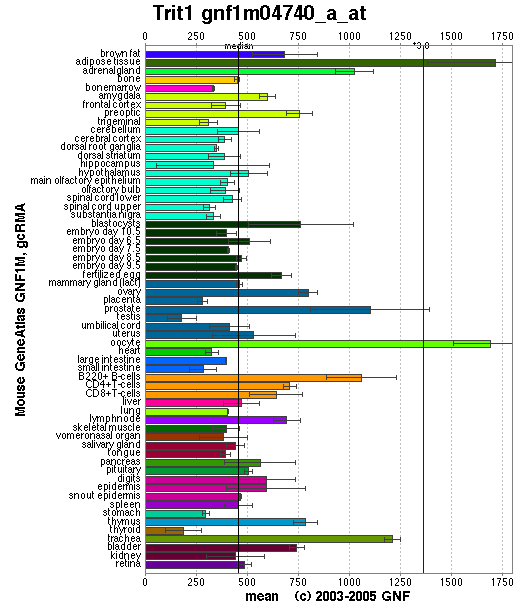
Generally, this enzyme is expressed in all tissue types since it is important that functional protein are synthesized in each of these tissues. Specifically, it is highly expressed in adipose tissues as well as oocytes. Relatively high amounts of this enzyme is expressed in prostate, adrenal gland, B-cells and trachea. The reason why tRNA-IPT are at higher concentrations in these tissues may reflect higher levels of protein synthesis. | Generally, this enzyme is expressed in all tissue types since it is important that functional protein are synthesized in each of these tissues. Specifically, it is highly expressed in adipose tissues as well as oocytes. Relatively high amounts of this enzyme is expressed in prostate, adrenal gland, B-cells and trachea. The reason why tRNA-IPT are at higher concentrations in these tissues may reflect higher levels of protein synthesis. | ||
Revision as of 05:23, 27 May 2008
Structure of tRNA isopentenyltransferase
Localisation Expression of tRNA isopentenyltransferase
Generally, this enzyme is expressed in all tissue types since it is important that functional protein are synthesized in each of these tissues. Specifically, it is highly expressed in adipose tissues as well as oocytes. Relatively high amounts of this enzyme is expressed in prostate, adrenal gland, B-cells and trachea. The reason why tRNA-IPT are at higher concentrations in these tissues may reflect higher levels of protein synthesis.
Domain and Structural Analysis
Structural Elements and Functional Binding Sites of tRNA isopentenyltransferase
-Residue Flexibility
-Hydrophobicity
LOCATE results show that this enzyme is soluble in nature; although a small part of the protein terminus is hydrophobic.
-Functional Sites Found By Pattern Search
Table 1
-Functional Sites Found by Sequence Conservation In Structurally Related Proteins -Functional Sites Found by Structure Conservation In Structurally Related Proteins -Multiple Sequence Alignment
Tree