Function: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 139: | Line 139: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Click here to go [http://compbio.chemistry.uq.edu.au/mediawiki/index.php/BIOL3004_2007 ''Back''] | |||
Revision as of 23:26, 10 June 2007
The predicted function based on the evolution and structure
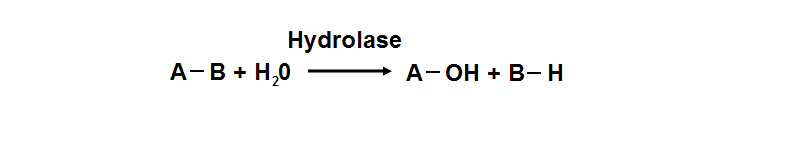
Hydrolyase
Hydrolyase catalyze the hydrosis of the chemical bond between A and B, resulting of 2 simple molecules
- Hydrolase
- Catalyze hydrolysis reaction
- Addition of the hydrogen and hydroxyl ions of water
- Splitting into 2 or more simpler molecules
- EC class 3
Gene Ontology
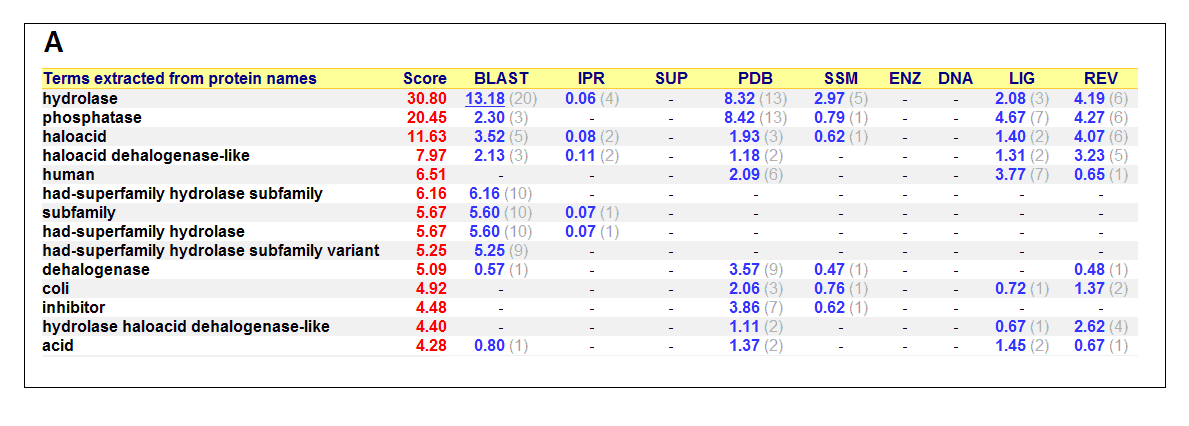
List of all matched protein name terms for 2gfh. The score in red is a measure of how strongly the term is predicted from the hits obtained by
the different methods. The scores in blue show each method’s contribution to the total score (with the number of relevant
sequences/structures shown in brackets in grey).(http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/)
- Higest score in GO - Hydrolase
- Followed by - Phosphatase
- Polymer: Haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain containing 4
- Molecular Function: None
- Biological Process: None
- Cellular Component: None
Surface Properties
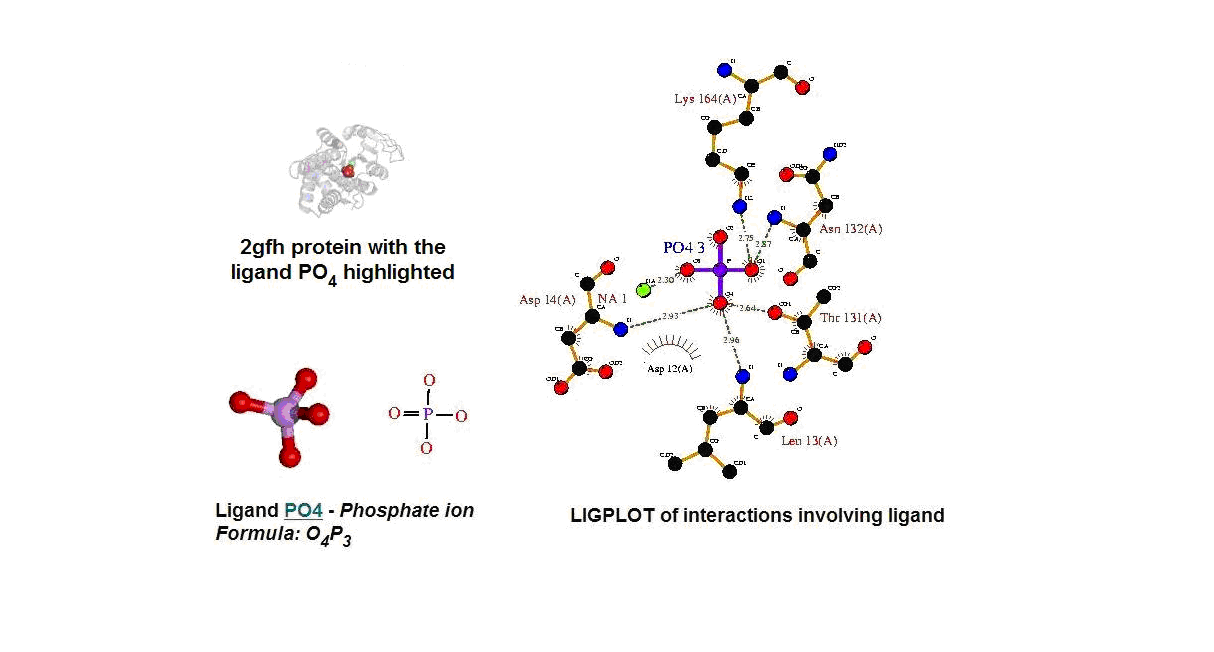 Figure 13. (A) Molecular structure of 2gfh with the ligand PO4. (B) Molecular and chemical structure of PO4. (C) Ligand interaction involving PO4. (Picture adapted from Profunc)
Figure 13. (A) Molecular structure of 2gfh with the ligand PO4. (B) Molecular and chemical structure of PO4. (C) Ligand interaction involving PO4. (Picture adapted from Profunc)
- Identify the likely biochemical function from the 3D structure
- Possible binding sites and potential ligands - PO4
- PO4 most likely be an active site and fuction
Phostphatase
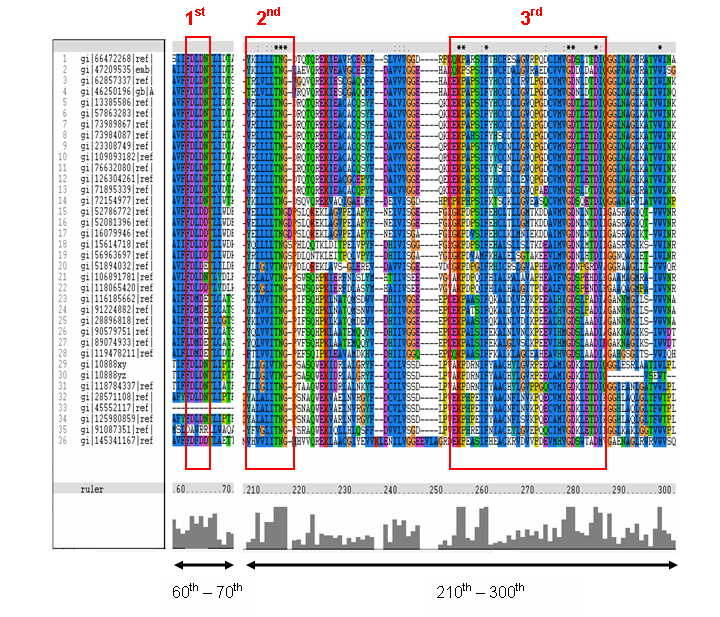
MSA of the 2gfh with 35 others proteins. Only the 60th – 70th and the 210th -300th amino acid
sequence were shown to illustrate the conserved and invariant regions. The 3 boxed-up sequences were either conserved or invariant regions.
- 1st - aspartic acid (D)
- 2nd - threonine (T), asparagine (N) and glycine (G)
- 3rd - lysine (K) and aspartates (D)
- MSA corelate with with study done by Maliekal et al
- N-acetylneuraminic acid phosphatase orthologs shared 3 motifs found in phosphatases
- HAD (Haloacid dehalogenase-like) family
- Phosphatase activity: CO–P bond hydrolysis
- Dehalogenase activity: C–halogen bond hydrolysis
- Phosphonatase: C–P bond hydrolysis
- Phosphoglucomutase: CO–P bond hydrolysis and intramolecular phosphoryl transfer
Role in Human
- OMIM
- Haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain
- Gene map locus 20p11
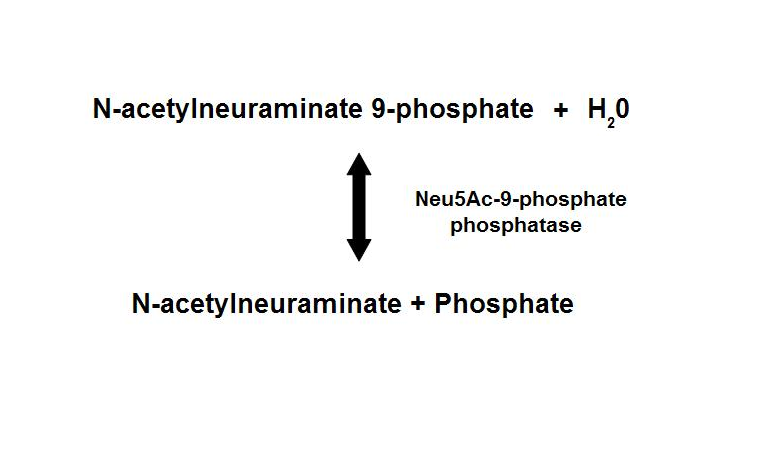
Dephosphorylation of Neu5Ac-9-P is a reversible reaction with an end product of Neu5Ac (sialic acid) and a free phosphate.
- Main form of sialic acid in vertebrates
- Important roles in protein-protein and cell-cell recognition
- Dependent on the presence of Mg2+
- Inhibited by vanadate and Ca2+
Role in Bacteria - E.coli
- Hydrolyze a wide range of phosphorylated metabolites
- Carbohydrates
- Nucleotides,
- Organic acids
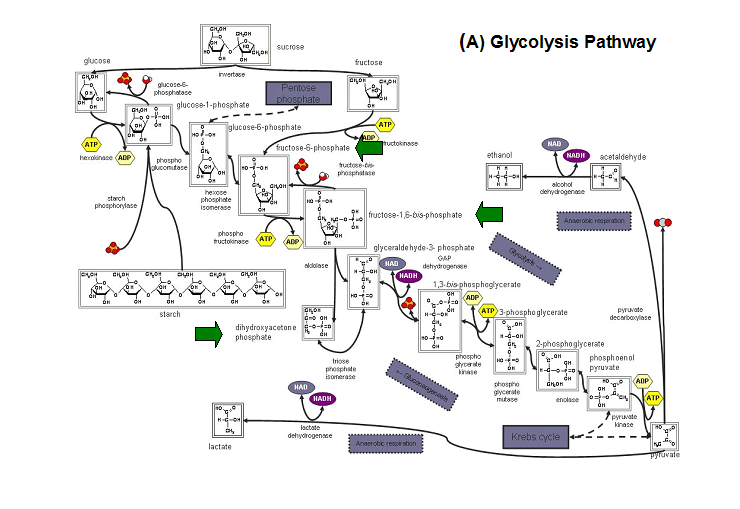
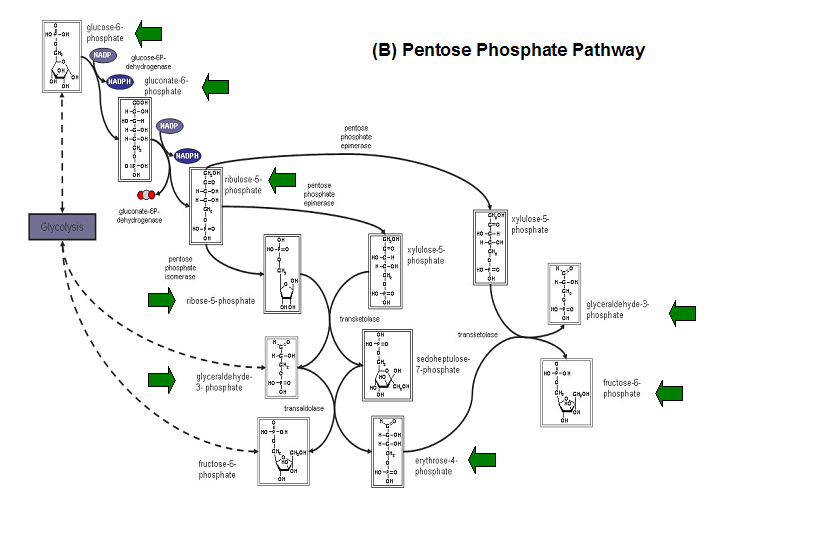
- Kuznetsova et al - glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathway
- Fructose-1-phosphate
- Glucose-6-phosphate
- Mannose-6-phosphate
- 2-deoxyglucose-6-phosphate
- Fructose-6- phosphate
- Ribose-5-phosphate
- Erythrose- 4-phosphate
Schematic diagrams of glycolysis and pentose phosphate metabolic pathways. The green arrows show the substrates that are hydrolyzed by HADs (http://www.steve.gb.com/science/core_metabolism.html)
Click here to go Back