Arylformamidase Structure: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
'''Archaeoglobus fulgidus Carboxylesterase (Chains A | '''Archaeoglobus fulgidus Carboxylesterase (Chains A)''' | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:ChainA 1jji.PNG]] '' From PDB ProteinWorkshop 1.5'' | ||
[[Image:Carboxylesterase (archaeon).txt]] | [[Image:Carboxylesterase (archaeon).txt]] | ||
Revision as of 02:12, 3 June 2008
1. Structure of Arylformamidase
Arylformamidase
The image above shows the chains A (upper right), B (upper left), C (lower right) & D (lower left) interacting. The molecules in the middle of chains A & B and chains C & D is phosphate ion (PO4). The green molecule between chain B & D is a magnesium ion (Mg). These ions aren't biologically significant and could only be an artefact. Those chains exist as indivitual functional units.
Chain A of arylformamidase
The red molecule in the middle is an unknown ligand containing a ring composed of 9 oxygen molecules. The green sphere is a chloride ion.
The protein backbone is coloured by conformation type:
Turn - blue
Coil- pink
Helix- green
strand- purple
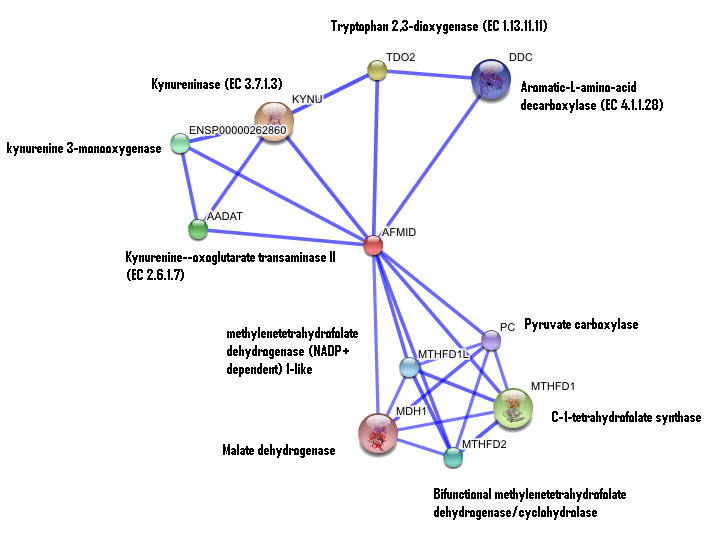
2. Interaction of human arylformamidase (AFMID) with other proteins
The interaction between the proteins have been determined from curated STRING database (significant score). However there is no significant evidence for:
1- Neighborhood in the genome
2- Gene fusions
3- Cooccurence across genomes
4- Co-Expression
5- Experimental/Biochemical data
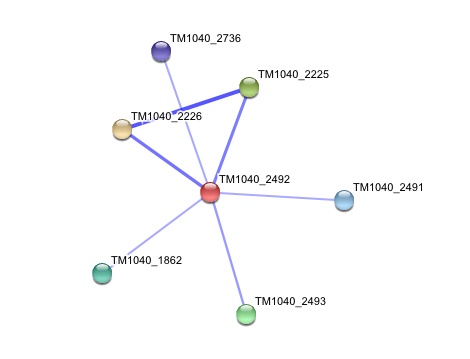
3. Interaction of Silicibacter Sp. arylformamidase (AFMID) with other proteins
TM1040_2226 Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (279 aa)
TM1040_2225 Kynureninase (396 aa)
TM1040_2493 Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (490 aa)
TM1040_1862 Hypothetical protein (212 aa)
TM1040_2491 Creatinase (402 aa)
TM1040_2736 Transketolase, putative (794 aa)
There is no significant evidence for these interactions (score= ~0.5)
4. DALI OUTPUT
The DALI tool produces proteins that are structurally similar to the protein of interest.
The search result showed similarities to mostly carboxylesterases/hydrolases. Hence there is strong evidence that our protein might also be a carboxylesterase.
Metagenomic Archea Carboxylesterase A chain
PDB link title
Archaeoglobus fulgidus Carboxylesterase (Chains A)
File:Carboxylesterase (archaeon).txt
PDB link title
These chains exist as monomers (from literature). Hence it is expected that our protein exists as a monomer but during crystalization it interacts with its chains.
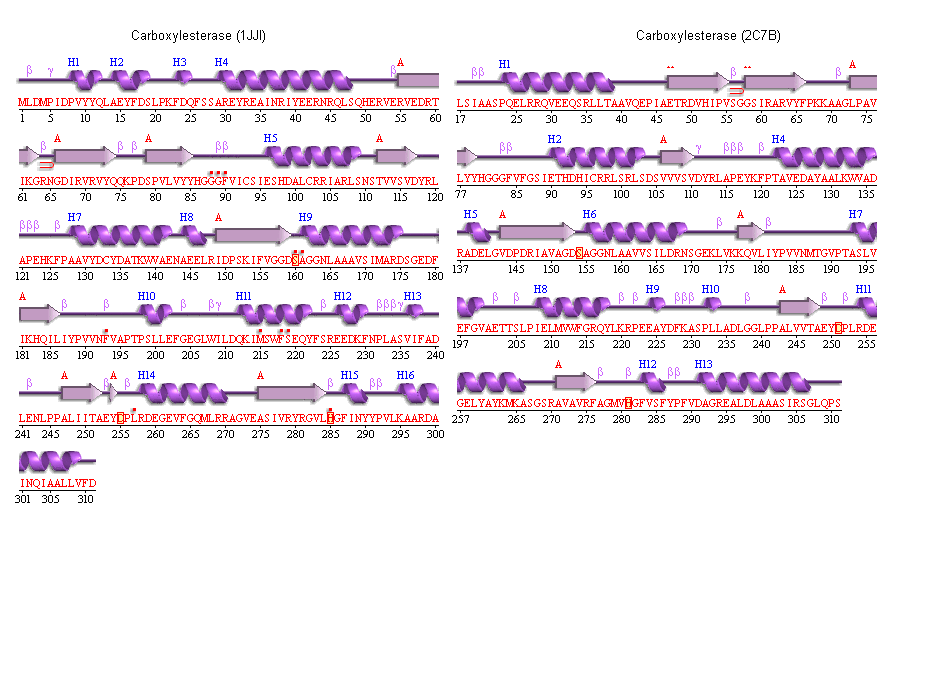
5. Secondary structure analysis
PDBSum output for arylformamidase
PDBSUM [1]
Archeon Carboxylesterase secondary structure
6. The conservation of the ser/his/asp catalytic triad
Yellow indicates conservation
Blue indicates semi-conservation
The above image shows the conserved residues of catalytic triad in arylformamidase, with the unknown ligand (Blue) protruding from a surface groove.
SER 136
HIS 241
GLU 214
The below image shows the distance between the catalytic triad conserved residues and how each amino acid is linked to a turn region.
Turn - blue
Coil- pink
Helix- green
strand- purple