Arylformamidase Function Slide 1: Difference between revisions
From MDWiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
Thomasparker (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Thomasparker (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
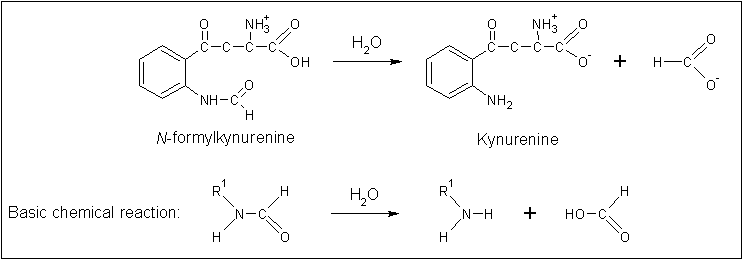
[[Image:Arylformadisae_reaction.gif|centre|framed|Reaction mechanism of the mammalian arylformamidase.]] | [[Image:Arylformadisae_reaction.gif|centre|framed|Reaction mechanism of the mammalian arylformamidase.]] | ||
- No evidence in this literature search suggested the existence of prokaryotic arylformamidase proteins | - No evidence in this literature search suggested the existence of prokaryotic arylformamidase proteins. | ||
[[Arylformamidase Function Slide 1 | ...Previous slide ]]|[[Arylformamidase| Return to the main page ]]|[[Arylformamidase Function Slide 2| Next slide... ]] | [[Arylformamidase Function Slide 1 | ...Previous slide ]]|[[Arylformamidase| Return to the main page ]]|[[Arylformamidase Function Slide 2| Next slide... ]] | ||
Revision as of 11:34, 8 June 2008
Literature Search
Keyword: Arylformamidase - putative function.
Returned:
Pabarcus MK, Casida JE. Cloning, expression, and catalytic triad of recombinant arylformamidase. Protein Expr Purif. Nov;44(1):39-44.
- Describes EstE1, an arylformamidase present in the liver of Mus musculus.
- Arylformamidase forms part of the tryptophan degradation pathway...
- No evidence in this literature search suggested the existence of prokaryotic arylformamidase proteins.