Paper
Evolution, Structure and Function of N-acetylneuraminic Acid Phosphatase
Jason Cheong Wen Leong (s41235935), Yau Heen wai (s41286272), Lim Junxian (s41313011)
Abstract
N-acetylneuraminic acid phosphatase a novel protein investigated by our group. With its structure and sequence known, the function was
assumed to be a part of the enormous family of haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolases. It represent the family of predicted small molecule
phosphatases related by sequence cleave sites and reactions in the genomes of bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Many have evolved to be used
for specific biological functions within individual organism
Introduction
The novel protein investigated by our group is N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) phosphatase, it was first release on Protein Data Bank
(PDB) on 18th April 2006, named 2gfh. Mus muscular (mouse) was used as the source of the gene and Escherichia coli was the
vector used to express the novel protein. In Homo sapiens (man), it was known to be as N-acetylneuraminate 9-phosphate (Neu5Ac-9-P)
phosphatase haloacid dehalogenase (HAD)-like hydrolase domain containing protein 4. Other aliases of the novel protein include C20orf147, NANP
and HDHD4. The gene encoding the protein was found to be on chromosome 20; location 20p11.1.
Neu5Ac-9-P phosphatase belongs to a large family of haloacid dehalogenase (HAD)-like hydrolases. The enzymes found within this classification
possess varied types of cleavage activities. Although many of its members are related by sequence cleave sites and reactions, many have evolved
to be used for specific biological functions within individual organisms.
These small molecule phosphatase enzymes have been found to exists in the various domains of life — Bacteria, Archaea, and Eucarya. The number
of genes found within each organism is varied from bacteria to eukaryotes. Bacterial Neu5Ac synthase and mammalian Neu5Ac-9-P synthase are
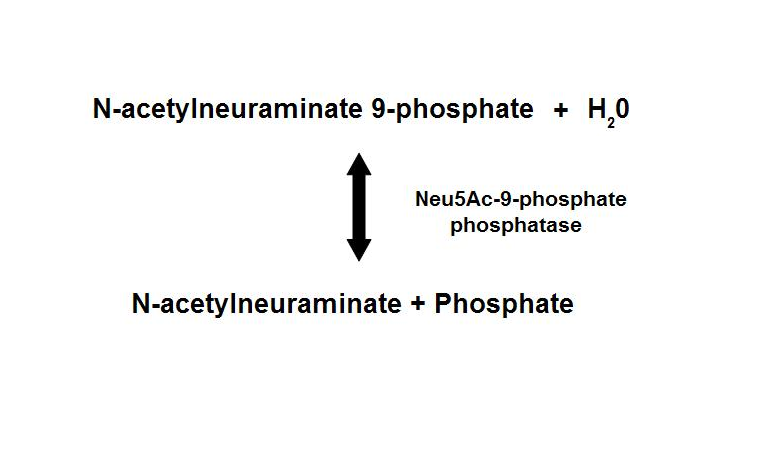
homologous proteins, sharing about 35% sequence identity1. Neu5Ac-9-P phosphatase dephosphorylates Neu5Ac-9-P to form Neu5Ac, the
main form of sialic acid.
Figure 1. Dephosphorylation of Neu5Ac-9-P is a reversible reaction with an end product of Neu5Ac (sialic acid) and a free phosphate.
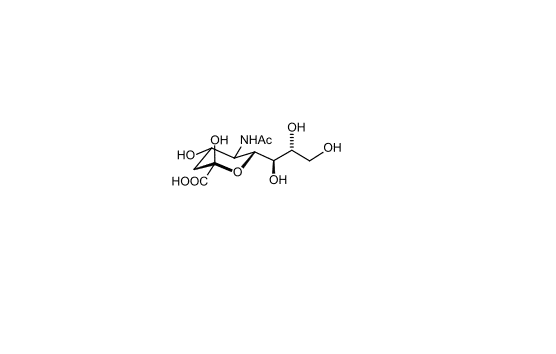
Sialic acids are nine-carbon sugars with a carboxylate group that are found as components of many glycoproteins, glycolipids, and
polysaccharides in animals, viruses, and bacteria. The main form of sialic acid, Neu5Ac, is often present as the terminal sugar of N-
glycans on glycoproteins and glycolipids and plays an important role in protein–protein and cell–cell recognition 2; 3.
Figure 2. Chemical structure of sialic acid.(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sialic_acid)
Sialic acids are found widely distributed in animal tissues and in bacteria, especially in glycoproteins and gangliosides. The amino group
bears either an acetyl or a glycolyl group. Sialic acid consists of acetylated, sulfated, methylated, and lactylated derivatives and is a large
family of more than 50 members 4.
Results
Query Sequence
The amino acid query sequence of 2gfh protein (Figure 3) from Mus musculus is obtained from Genbank.
| <1 mgsdkihhhh hhmglsrvra vffdldntli dtagasrrgm levikllqsk yhykeeaeii
61 cdkvqvklsk ecfhpystci tdvrtshwee aiqetkggad nrklaeecyf lwkstrlqhm 121 iladdvkaml telrkevrll lltngdrqtq rekieacacq syfdaivigg eqkeekpaps 181 ifyhccdllg vqpgdcvmvg dtletdiqgg lnaglkatvw inksgrvplt sspmphymvs 241 svlelpallq sidckvsmsv> |
Figure 3. The 260 amino acid sequence of 2gfh protein.
Sequence Homology
From the BlastP similarity was used for comparison as these had shown higher homology to the query sequence sequence search, a total of 500
proteins were yielded.Only a total of 38 proteins, in contrast with the remainder of the search results.These proteins were chosen according to
their bit scores and E-values. Two more outlier partial sequences contributing to poor overall alignment (huge deletion gaps) were subsequently
removed. The remaining 36 sequences were used for the generation of the phylogenetic tree (and bootstrapped tree as well).
Multiple Sequence Alignment
The following multiple sequence alignment (MSA) was obtained (Figure 4). From the alignments, gi|10888xy and
gi|10888yz are representative of gi|108881764 and gi|108881765 respectively. Both these
hypothetical proteins belong to the mosquito Aedes aegypti.
The identifier numbers for these two proteins were initially changed to an alpha-numeric one, due to the inability of Phylip to generate a tree
from the original identifiers. This was due to the fact that the programme only took the first five numeric digits (10888), thereby resulting
in a programme error prompt which listed both proteins as duplicates (from the identifier numbers). Both these identifiers were subsequently
renamed for the final phylogenetic tree.
Figure 4. MSA of query (top-most sequence – No.1) and related sequences.
From the MSA, it can be observed that there are generally slight domain conservations throughout the protein sequences. Small insertion and
deletion gaps were noticeable along the alignment as well. A particularly large insertion gap was observed between amino acids 91 to 114.
The organisms with the large insertion gaps were as identified below:
Bacillus licheniformis
Bacillus subtilis
Bacillus halodurans
Bacillus clausii
Symbiobacterium thermophilum
A highly conserved (with invariant) section of amino acids (LV)–(LVA)–(LIV)–(LIV)-T-N-G was observed in all the sequences from amino acid 211
to 217 in the alignment. Downstream of this conserved portion of genes are 5 more invariant positions (1 or 2 amino acids in length).From these
short conservation regions, the functions or even structure of the encoded proteins could have significance in its evolutionary pattern.
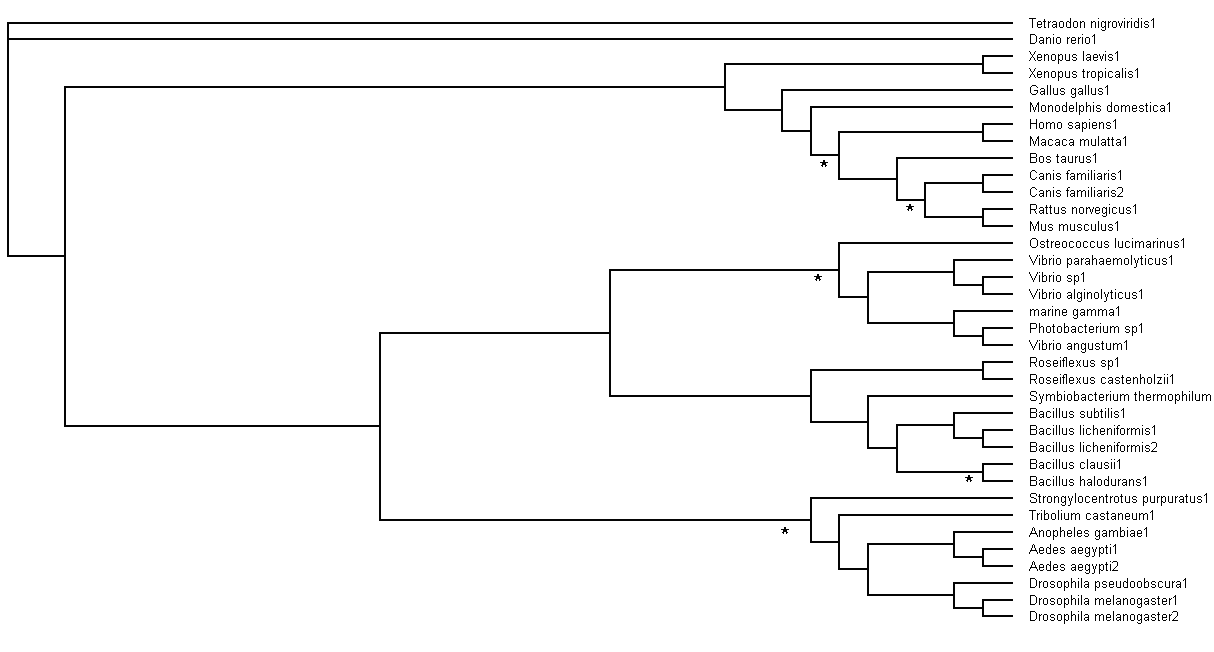
Phylogenetic Tree
The tree was plotted to obtain the phylogenetic lineage (Figure 5).
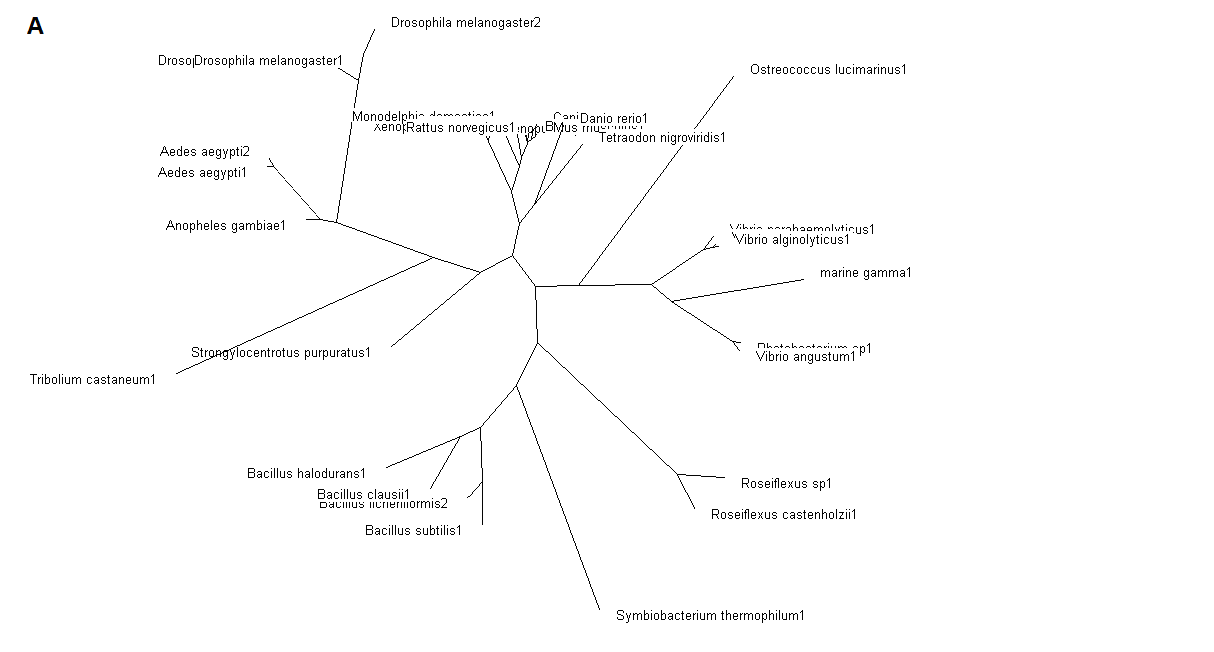
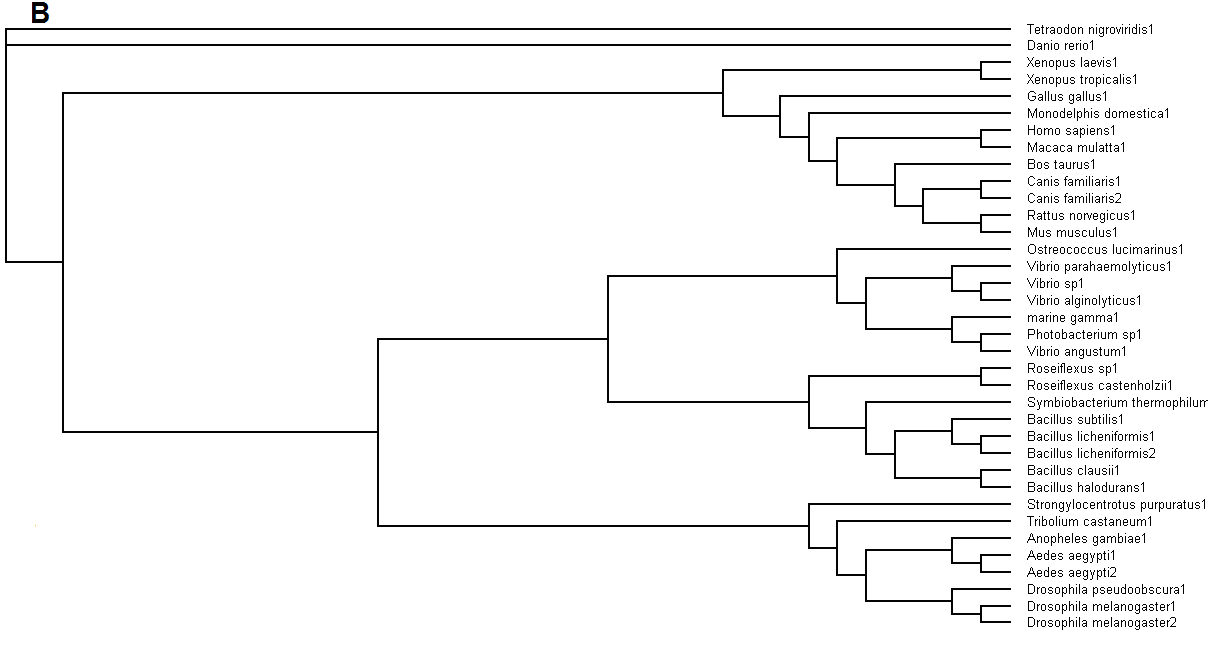
Figure 5. (A) Phylogenetic tree showing organisms with related protein sequence homology in Radial Tree view. (B) Rectangular
Cladogram view with related protein sequence homology.
From the Rectangular Cladogram view, it could be observed that there are four distinct separate groups involving fishes, mammals (where the
query protein is also mapped), bacteria and insects.
Bootstrapping
Bootstrapping values obtained were analysed. Branch values occurring below 75% (<75%) would be indicated by an asterisk (*),
as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6. Branch bootstrap values in Rectangular Cladogram view. Branches with strap values <75% were indicated with
asterisks (*)
DALI Searching
SUMMARY: PDB/chain identifiers and structural alignment statistics NR. STRID1 STRID2 Z RMSD LALI LSEQ2 %IDE REVERS PERMUT NFRAG TOPO PROTEIN
1: 3033-A 2gfh-A 41.1 0.0 246 246 100 0 0 1 S HYDROLASE haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain 2: 3033-A 1fez-A 18.1 3.5 178 256 22 0 0 13 S HYDROLASE phosphonoacetaldehyde hydrolase (bacillus c 3: 3033-A 2hsz-A 17.9 3.3 168 222 23 0 0 13 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION novel predicted 4: 3033-A 1qq5-A 17.3 3.1 198 245 19 0 0 12 S HYDROLASE l-2-haloacid dehalogenase (xanthobacter aut 5: 3033-A 1o03-A 17.0 5.0 188 221 20 0 0 11 S ISOMERASE beta-phosphoglucomutase (lactococcus lactis 6: 3033-A 2b0c-A 16.4 2.6 184 199 20 0 0 13 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION putative phospha 7: 3033-A 2fdr-A 15.8 4.4 190 214 19 0 0 15 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION conserved hypoth 8: 3033-A 2p11-A 15.7 2.9 194 211 16 0 0 20 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro 9: 3033-A 1te2-A 15.7 3.6 170 211 19 0 0 15 S HYDROLASE putative phosphatase (escherichia coli o157 10: 3033-A 1yns-A 15.3 4.0 169 254 11 0 0 13 S HYDROLASE e-1 enzyme (enolase-phosphatase e1) (homo s 11: 3033-A 1qyi-A 15.0 3.5 198 375 19 0 0 17 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro 12: 3033-A 2i6x-A 14.9 3.1 176 199 19 0 0 18 S HYDROLASE hydrolase, haloacid dehalogenase-like family 13: 3033-A 1u7p-A 14.3 2.9 144 164 18 0 0 14 S HYDROLASE magnesium-dependent phosphatase-1 (mdp-1) ( 14: 3033-A 1ymq-A 14.1 2.3 130 260 16 0 0 14 S TRANSFERASE sugar-phosphate phosphatase bt4131 (bacte 15: 3033-A 1j8d-A 13.1 2.5 141 180 11 0 0 12 S HYDROLASE deoxy-d-mannose-octulosonate 8-phosphate ph 16: 3033-A 2ho4-A 12.9 2.4 131 246 19 0 0 14 S HYDROLASE haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain 17: 3033-A 1pw5-A 12.7 2.3 136 246 21 0 0 12 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION nagd protein, pu 18: 3033-A 1nf2-A 12.7 2.6 127 267 13 0 0 11 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS/UNKNOWN FUNCTION phosphatase (the 19: 3033-A 1rlm-A 12.4 2.8 131 269 13 0 0 14 S HYDROLASE phosphatase Mutant (escherichia coli) bacte 20: 3033-A 1f5s-A 12.1 3.5 159 210 14 0 0 15 S HYDROLASE phosphoserine phosphatase (psp) (methanoco 21: 3033-A 1cr6-B 12.0 3.8 177 541 18 0 0 18 S HYDROLASE epoxide hydrolase (mus musculus) mouse expr 22: 3033-A 1rku-A 11.9 3.6 172 206 11 0 0 18 S TRANSFERASE homoserine kinase (pseudomonas aeruginosa 23: 3033-A 2b30-A 11.8 2.7 134 284 16 0 0 12 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION pvivax hypotheti 24: 3033-A 1kyt-A 10.5 2.5 122 216 13 0 0 15 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro 25: 3033-A 2o2x-A 10.3 3.6 139 204 17 0 0 14 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro 26: 3033-A 1u02-A 10.1 2.7 128 222 16 0 0 12 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase 27: 3033-A 2fea-A 10.0 3.5 167 219 7 0 0 21 S HYDROLASE 2-hydroxy-3-keto-5-methylthiopentenyl-1- pho 28: 3033-A 2hx1-A 9.6 3.2 130 275 24 0 0 19 S HYDROLASE predicted sugar phosphatases of the had supe 29: 3033-A 1mh9-A 9.2 3.2 146 194 15 0 0 15 S HYDROLASE deoxyribonucleotidase (mitochondrial 5'(3')-
Figure 7. The DALI search results that were returned through e-mailed. The highlighted (yellow) shows the query protein. With a z value
of 41.1 and a root mean standard deviation of 0.0 and %IDE of 100, shows that it is a HAD family protein. The highlighted (green) shows
significant similarities of query protein as a hydrolase phosphatase as Z values are more then 1, RMSD still of low values and %IDE of more
then 20.Z
From the DALI search (Figure 7), Neu5Ac phosphatase is a haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase. This family is structurally different from the
alpha/ beta hydrolase family. It has L-2-haloacid dehalogenase, epoxide hydrolases and phosphatases. This family consists of two domains of
structure. One is an inserted four helix bundle, which is the least well conserved region of the alignment, between residues 16 and 96 of (S)-2-
haloacid dehalogenase I. The remaining of the fold is composed of the core alpha/beta domain. It is classified as a hydrolase found in mouse.
The chemical components would be phosphate ion, sodium ion, 1,2-ethanediol, chloride ion. PO4 and EDO are ligands while
Na and Cl are metals.