Pyridoxal Phosphatase Discussion
Evolution
Structure
PDB
Based on the information obtained from PDB, 2cfsA was identified to have the following features:
- Isolated from Homo Sapiens, and is expressed in Escherichia Coli.
- Structurally similar to the Pyridoxal Phosphate Phosphatase protein.
- Consists of a single type of chain (A), and (2) Magnesium components.
- Resolution of 2.4 angstroms. The significance of this is that the probability that the number of side-chains in the wrong rotamer is relatively smaller. Proteins of similar resolution were noted also to: (1) have many small detectable errors, (2) be of correct folding, (3) contain fewer number of errors in the surface loops and (4) consist of visible water molecules and small ligands.
DALI
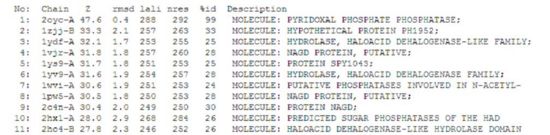
A search on the protein in the Dali database yielded 176 hits, of which the top 11 were identified to be of potential significance on account of the information provided in the summary block of the results. The summary block provides the following information:
- Z score, or the statistical significance of the similarity between the hit protein and the protein-of-interest.
- Root Mean Square Distance (RMSD), which indicates the degree of divergence between the hit protein and the protein-of-interest.
- lali, the total number of shared residues between the hit protein and the protein-of-interest.
- nres, or the total number of residues in the hit protein.
- %id. As the term implies, %id refers to the percentage of sequence identity over structurally identical positions.
Of the 11 hit proteins, 2oycA was predicted to be the most structurally similar to 2cfsA. This was on virtue of the following properties:
- Among the list of hit proteins generated, it had the highest Z value of 47.6
- rmsd value of 0.4, the lowest among the hit proteins. The lower the rmsd value, the more similar it is to the protein-of-interest.
- lali value of 288. 2cfsA has a total of 298 amino acid residues, which means that 2oycA and 2cfsA differ by only 10 amino acid residues.
- nres value of 292. This did not bear much significance on the decision-making process. However, a conclusion drawn was that it was similar to 2cfsA in terms of length.
- %id score of 99%, which simply means that based on the information currently stored in the DALI database, 2oycA and 2cfsA were highly similar.
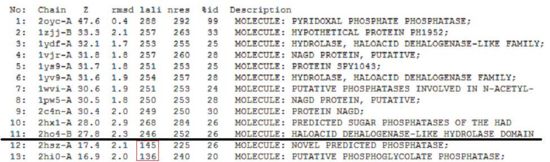
Given that 2cfsA has 298 amino acid residues, the twelfth hit onwards (i.e. 2hszA) were rejected as more than half of their amino acid residues did not indicate similarity to 2cfsA.
To further prove that 2cfsA and 2oycA were structurally similar, their three dimensional structures were superimposed using PyMOL. As expected, the 2oycA bore a close resemblance to 2cfsA, but the differing regions have yet to be identified.
PDBsum
The secondary structures of 2cfsA and 2oycA were noted to be highly similar, the only difference being that 2oycA did not have any disulphide bonds, nor indications of any active site(s), as opposed to 2cfsA.
The topology diagrams, however, indicated complete homology between the said proteins.
A cleft analysis for both proteins was conducted, and based on the three-dimensional modelling using PyMOL, it was concluded that both proteins may have similar active sites. This is significant as structural information is usually crucial for the functional prediction of the protein-of-interest. Since the information provided by the secondary structures of both proteins are highly similar, there is a great possibility that 2cfsA and 2oycA are functionally similar.
PROFUNC
Based on the results generated by DALI, it was concluded that 2cfsA and 2oycA were structurally similar and this could have been a crucial point in the functional determination of both proteins. A search on Profunc, however, seemed to suggest that 2cftA is a much closer match to 2cfsA than 2oycA. In fact, 2cftA can be said to be identical, in more ways than one, to 2cfsA.
It was important to note that unlike the information provided by NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/viewer.fcgi?db=protein&val=134104092), 2cfsA was noted to have 293 amino acid residues instead of 298 (NCBI). One reason for this discrepancy could be that in the ever-changing scientific field, existing information will not be spared from change.
Based on the information provided by PDB, 2cfsA and 2cftA shared identical sequences and structures. However, this does not rule out 2oycA, as it was still the next closest protein hit to 2cfsA and 2cftA.
In terms of secondary structure matching (SSM), however, 2cftA was NOT identical to 2cfsA, even though it was homologous enough to be ranked as the next highest protein hit. 2oycA was a distant sixth on the list, four tiers below 2cftA. Such was the homology of all the hit proteins, however, that even at sixth, the deviation between 2cfsA and 2oycA was minimal.
To determine the potential active sites of 2cfsA, the nest analysis method was utilized. Based on an article by Pal et. al, 2002, the principle of this method revolves around the possibility that anion (negatively-charged) and cation (positively-charged) binding sites in proteins are made up of three amino acids, of which two exhibit "enantiomeric" main chain conformations. This simply means that the main chain torsion angles of the two adjacent amino acids are inverted about the centre of the Ramachandran plot. This results in the formation of "nests", which are defined as concave depressions which ultimately serve as binding sites.
A search on 2oycA was then done on PROFUNC, the following were confirmed:
- 2oycA is structurally similar to 2cfsA
- High probability of being functionally related due to common active sites
Function