Background info/Introduction: Difference between revisions
JasonCheong (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
JasonCheong (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The novel protein being investigated by our group is '''''N''-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) phosphatase''', named 2gfh. ''Mus muscular'' (mouse) was used as the source of the gene and protein expression was carried out through ''Escherichia coli''. In ''Homo sapiens ''(man), it was known to be as '''''N''-acetylneuraminate 9-phosphate (Neu5Ac-9-P)phosphatase haloacid dehalogenase (HAD)-like hydrolase domain containing protein 4'''. Other aliases of | The novel protein being investigated by our group is '''''N''-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) phosphatase''', named 2gfh. ''Mus muscular'' (mouse) was used as the source of the gene and protein expression was carried out through ''Escherichia coli''. In ''Homo sapiens ''(man), it was known to be as '''''N''-acetylneuraminate 9-phosphate (Neu5Ac-9-P)phosphatase haloacid dehalogenase (HAD)-like hydrolase domain containing protein 4'''. Other aliases of this protein include C20orf147, NANP and HDHD4. | ||
possess varied types of cleavage activities | NANP belongs to a large family of haloacid dehalogenase (HAD)-like hydrolases. The enzymes found within this classification | ||
possess varied types of cleavage activities, many of which has related sequence cleave sites and reactions. | |||
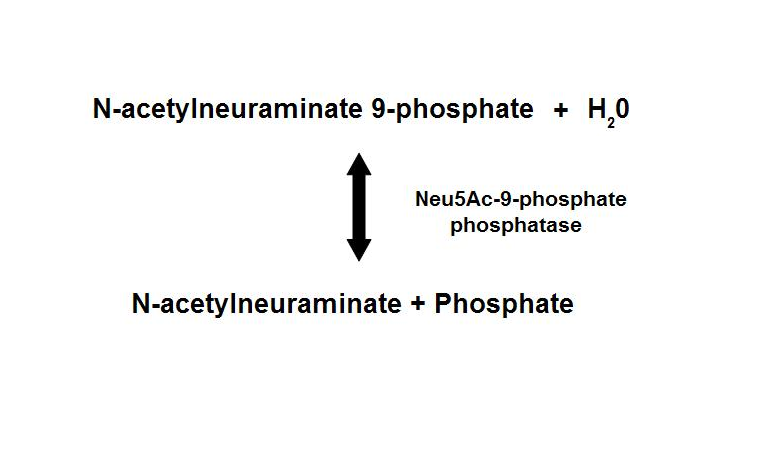
These enzymes have been found to exists in the various domains of life — Bacteria, Archaea, and Eucarya. The number of genes found within each organism is varied from bacteria to eucaryotes. Bacterial Neu5Ac synthase and mammalian Neu5Ac-9-P synthase are homologous proteins, sharing about 35% sequence identity. Neu5Ac-9-P phosphatase dephosphorylates Neu5Ac-9-P to form Neu5Ac, the main form of sialic acid. | |||
These | |||
of genes found within each organism is varied from bacteria to | |||
homologous proteins, sharing about 35% sequence identity | |||
main form of sialic acid. | |||
[[Image:Document2_01.png]] | [[Image:Document2_01.png]] | ||
| Line 20: | Line 12: | ||
'''Figure 1. ''' Dephosphorylation of Neu5Ac-9-P is a reversible reaction with an end product of Neu5Ac (sialic acid) and a free phosphate. | '''Figure 1. ''' Dephosphorylation of Neu5Ac-9-P is a reversible reaction with an end product of Neu5Ac (sialic acid) and a free phosphate. | ||
[[Image:Document5_01.png|framed|none]] | [[Image:Document5_01.png|framed|none]] | ||
| Line 31: | Line 17: | ||
Latest revision as of 03:51, 12 June 2007
The novel protein being investigated by our group is N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) phosphatase, named 2gfh. Mus muscular (mouse) was used as the source of the gene and protein expression was carried out through Escherichia coli. In Homo sapiens (man), it was known to be as N-acetylneuraminate 9-phosphate (Neu5Ac-9-P)phosphatase haloacid dehalogenase (HAD)-like hydrolase domain containing protein 4. Other aliases of this protein include C20orf147, NANP and HDHD4.
NANP belongs to a large family of haloacid dehalogenase (HAD)-like hydrolases. The enzymes found within this classification
possess varied types of cleavage activities, many of which has related sequence cleave sites and reactions.
These enzymes have been found to exists in the various domains of life — Bacteria, Archaea, and Eucarya. The number of genes found within each organism is varied from bacteria to eucaryotes. Bacterial Neu5Ac synthase and mammalian Neu5Ac-9-P synthase are homologous proteins, sharing about 35% sequence identity. Neu5Ac-9-P phosphatase dephosphorylates Neu5Ac-9-P to form Neu5Ac, the main form of sialic acid.
Figure 1. Dephosphorylation of Neu5Ac-9-P is a reversible reaction with an end product of Neu5Ac (sialic acid) and a free phosphate.
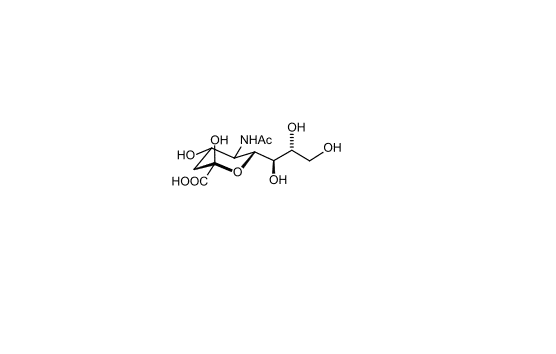
Figure 2. Chemical structure of sialic acid.(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sialic_acid)
Proceed to Evolution