Pyridoxal Phosphatase function
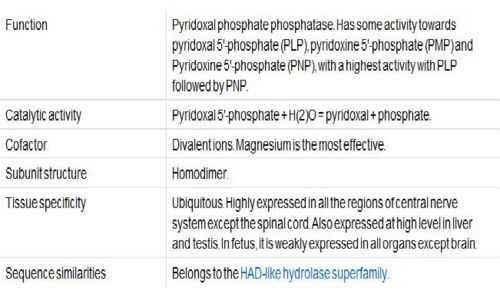
Vitamin B6, Pyridoxal Phosphatase, generally functions as a coenzyme for many reactions and can help facilitate decarboxylation, transamination, racemization, elimination, replacement and beta-group interconversion reactions. The Enzyme Commission (EC; http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iubmb/enzyme/ ) has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. To help predict any unknown functions of Pyridoxal Phosphatase, sequence homology, structural similarities, neighbouring genes, expression level in tissue and protein-protein interactions were analysed.
General Annotation
Known Functions
Amino Acid Metabolism
2cfsA is involved in almost all amino acid metabolism. Some of these amino acid metabolism include transamination, transsulfuration, selenoamino acid metabolism and conversion of typtophan to niacin.
Gluconeogenesis
2cfsA can catalyse transamination reactions that are essential for providing amino acids as a substrate for gluconeogenesis. 2cfsA is also required as a coenzyme for glycogen phosphorylase, which in turn catalyse glycogenolysis.
Neurotransmitter Synthesis
Pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzymes catalyses the biosynthesis of serotonin, epinephrine, norepinephrine and gamma-aminobutyric acid(The four important neurotranmsitters).
Histamine Synthesis
2cfsA is involved in the metabolism of histamine.
Hemoglobin Synthesis and Function
Pyridoxal phosphate aids in the synthesis of heme and can also bind to two sites on hemoglobin to enhance the oxygen binding of hemoglobin.
Gene Expression
Pyridoxal phosphate has been implicated in increasing or decreasing the expression of certain genes. Increased intracellular levels of 2cfsA will lead to a decrease in the transcription of glucocorticoid hormones. Also, vitamin B6 deficiency will lead to the increased expression of albumin mRNA. Also, pyridoxal phosphate will influence gene expression of glycoprotein IIb by interacting with various transcription factors. The result is inhibition of platelet aggregation.
Sequence homology
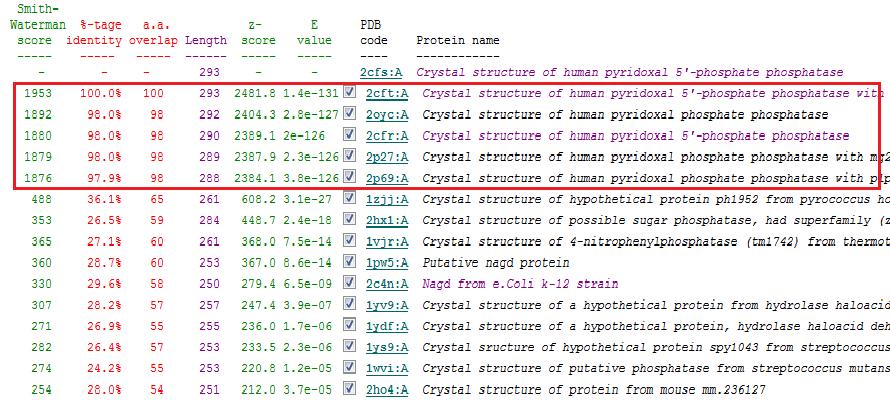
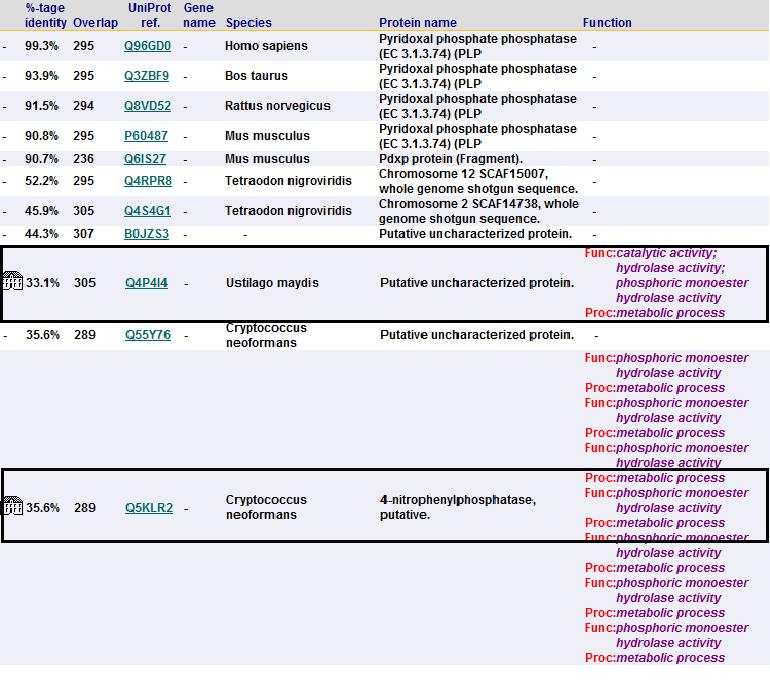
To check for function among similar homologs, 2cfsA sequence was run against FASTA, Pfam and PSI Blast non-redundant database. A search using Pfam and BLAST revealed that 2cfsA belonged to the superfamily, Haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase. It is noted that the top 15 search results from BLAST database all belong to the same superfamily, HAD-like hydrolase. Results from FASTA (below) also showed five results with almost identical sequence, all being HAD-like hydrolases.
Structural Similarities
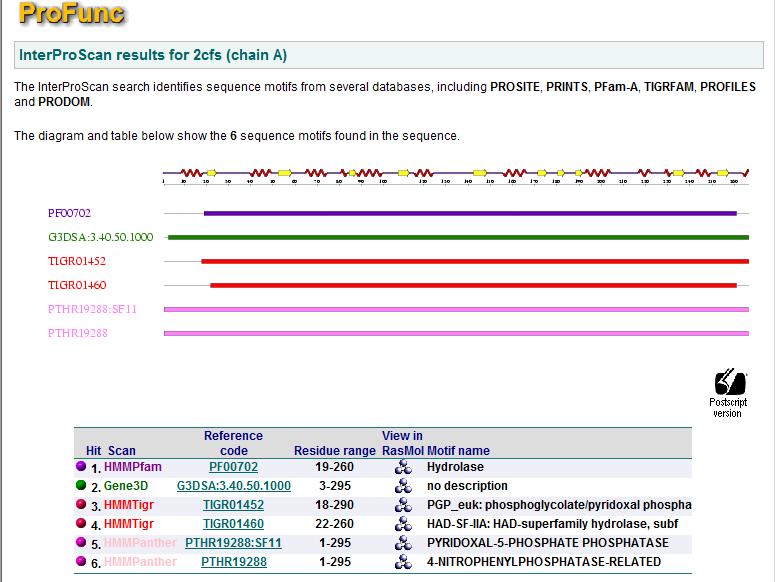
A search based on motifs resulted in six hits. Five of which are hydrolases and one with function unknown. Proteins with similar motifs does not suggest any other function for 2cfsA.
Location of Gene on Genome
It was noted that neighbouring genes also belongs to the same super family, HAD-like hydrolase.
Functional Expression in Tissue
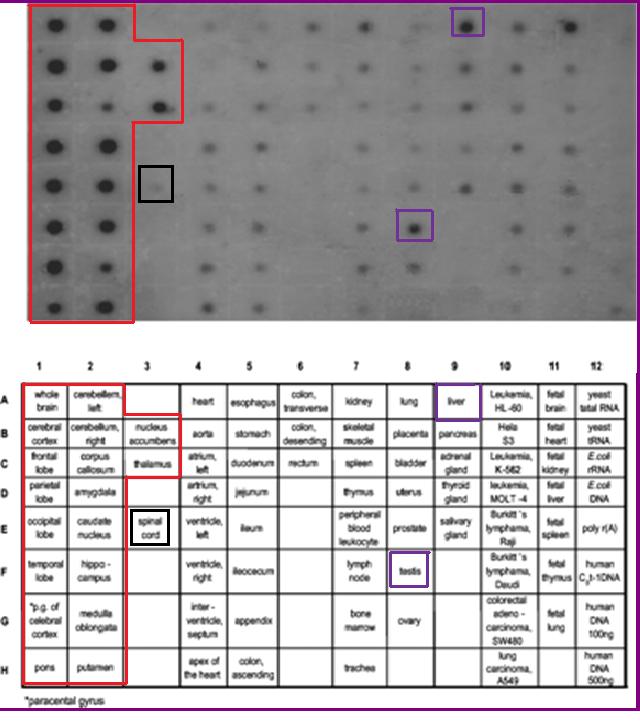
The mRNA expression levels of 2cfsA is experimentally proven to be ubiquitous. This is consistent with its essential role in cellular metabolism. However, 2cfsA may have a more specific function in the brain, where the expression level is substantially higher.(Young M. J. et al, 2003)
Protein-Protein Interactions
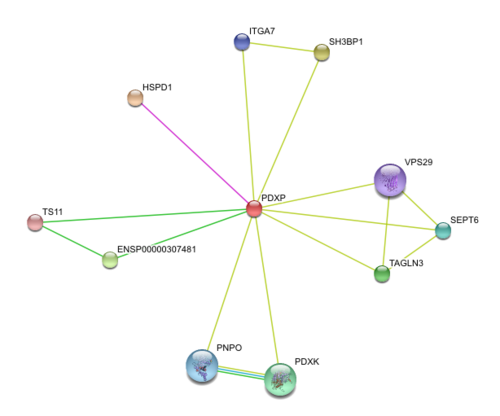
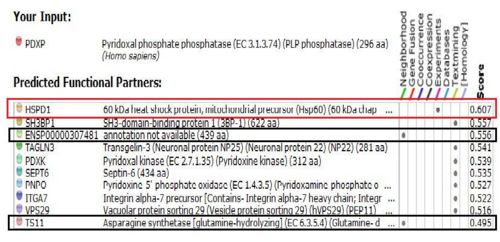
Results from STRING showed 11 predicted functional partners with a medium confidence score of >0.4. Of these 11, putative homologs of HSPD1, a chaperonin, was found to interact with PDXP in E coli K12, two were neighbour genes in 16 and 18 different genomes and eight were found by textmining. The eight were not considered due to lack of evidence. Homolog interactions suggests that 2cfsA maybe a cofactor of HSPD1 and play a role in protein folding. The search also revealed that TS11 is a neighbour gene for 2cfsA for 16 different genomes, hence it is possible that 2cfsA may actually bind to TS11 and function as a coenzyme for asparagine synthetase.
http://string.embl.de/newstring_cgi/show_network_section.pl?taskId=ph89gQxcLucL&allnodes=1
Back To Main Page | Back [Structure] | Back to BIOL3004 2008