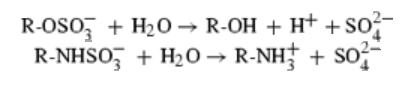3bsqA Results
Multiple sequence alignment
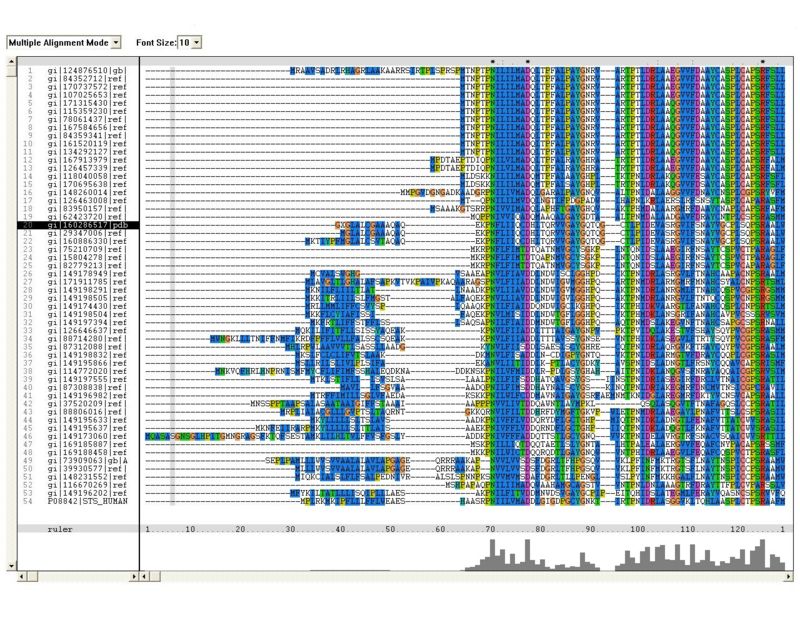
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) highlighted several residues in N-terminal region of the molecule which are highly conserved (figure 1).
Figure 1: Multiple sequence alignment (MSA). Residues which are concerved across the entire sulfatase family are marked in red
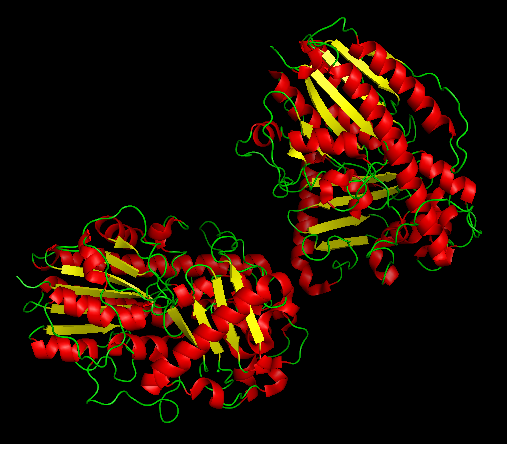
Arylsulfatase K structure
Protein data bank profile characteris arylsulfatase as a hydrolase and a sulfatase. A Sulfatase hydrolyses sulfate esters bonds of substrates, including O-sulfates and N-sulfates as shown below.
Structural alignment
- Three dimentional structure of arylsulfatase was aligned with other available structures using DALI server (structural alignment). Results are shown in 'figure 3'.
No: Chain Z rmsd lali nres %id Description 1: 3b5q-A 73.6 0.0 464 464 100 MOLECULE: PUTATIVE SULFATASE YIDJ; 2: 3b5q-B 70.2 0.3 464 467 100 MOLECULE: PUTATIVE SULFATASE YIDJ; 3: 2qzu-A 35.1 2.5 375 465 25 MOLECULE: PUTATIVE SULFATASE YIDJ; 4: 1fsu 28.7 2.8 344 474 22 MOLECULE: N-ACETYLGALACTOSAMINE-4-SULFATASE; 5: 1n2l-A 28.4 3.0 343 483 25 MOLECULE: ARYLSULFATASE A; 6: 1n2k-A 28.1 3.1 342 482 25 MOLECULE: ARYLSULFATASE A; 7: 1e2s-P 28.1 3.0 341 481 26 MOLECULE: ARYLSULFATASE A; 8: 1e3c-P 28.0 3.1 341 481 26 MOLECULE: ARYLSULFATASE A; 9: 1e33-P 28.0 3.1 342 480 25 MOLECULE: ARYLSULFATASE A; 10: 1e1z-P 27.9 3.0 341 481 26 MOLECULE: ARYLSULFATASE A; 11: 1auk 27.8 3.1 340 481 26 MOLECULE: ARYLSULFATASE A; 12: 1p49-A 27.7 2.9 338 548 24 MOLECULE: STERYL-SULFATASE; 13: 1hdh-B 27.4 3.1 365 525 23 MOLECULE: ARYLSULFATASE; 14: 1hdh-A 27.4 3.0 363 525 23 MOLECULE: ARYLSULFATASE; 15: 2rh6-A 24.3 2.6 257 382 14 MOLECULE: PHOSPHODIESTERASE-NUCLEOTIDE PYROPHOSPHATASE; 16: 2rh6-B 24.2 2.6 257 382 14 MOLECULE: PHOSPHODIESTERASE-NUCLEOTIDE PYROPHOSPHATASE;
figure 3: Structural alighment of ASK. 3b5q-A and B are two chains of ASK dimer and 2qzu-A is ASK of Bacterioides fragilis. N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase, Arylsulfatase A and steryl sulfatase, also known as stroid sulfatase (STS) are most structurally similar proteins to ASK. 1hdf is the ASK of Pseudomonal auruginosa.
- Arylsulfatase A has both sulfuric ester hydrolase and phosphoric monoester hydrolase activities and localised in lysosomes.
- Steryl-sulfatase is a sulfuric ester hydrolase found in endoplasmin reticulums.
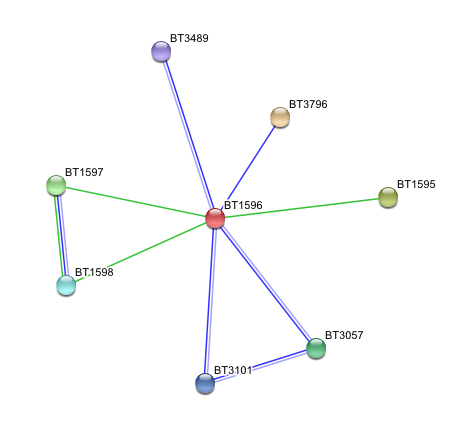
Arylsulfatase K interactions with other proteins
Subcellular interactions of arylsulfatase K were searched usnig the programme STRING, based on 'neighbourhood', 'cooccurreance' and 'homology' evidence. Results are shown below.
Input Protein
- BT1596 Putative sulfatase yidJ (481 aa) of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron.
Predicted Functional Partners
- BT3796: Putative secreted sulfatase ydeN (518 aa).
- BT1595 Transcription termination factor rho (722 aa).
- BT1597 Two-component system sensor histidine kinase (539 aa).
- BT3057 N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase (508 aa).
- BT1598 Putative two-component system sensor histidine (655 aa).
- BT3101 N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase (455 aa).
- BT3489 Arylsulfatase B {UniProtKB/TrEMBL-Q8A219} (458 aa).
'Putative secreted sulfatase ydeN' only showed neignbourhood relationship, which means that two genes are located in close proximity. In contrast, three of other proteins showed both cooccurrence and homology evidence.
ProFunc results for ASK interacting proteins.
- N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase cleaves the 6-sulfate groups of N-acetyl-D-galactosamine 6-sulfate units in chondroitin sulfate and D-galactose 6-sulfate units in keratan sulfate.
- N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase is also known as heparine sulfamidase, which catalyses the hydrolysis of Sulfur-Nitrogen bonds. N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase is responsible for the degradation of glucosaminlglycan and glycan structure of extra cellular matrix.
- N-acetylgalactosamine-4- sulfatase (Arylsulfatase B) hydrolyse the sulfate ester group from N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate of dermatine sulfate. Deficiency of ASB cause a rare mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS IV; Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome)
Two sequence alignment of ASK and STS
STS was chosen to be the most similar enzyme to ASK due to the shired subcellylar localization. Two sequence alignmnt between ASK and STS is shown is figure: 5.
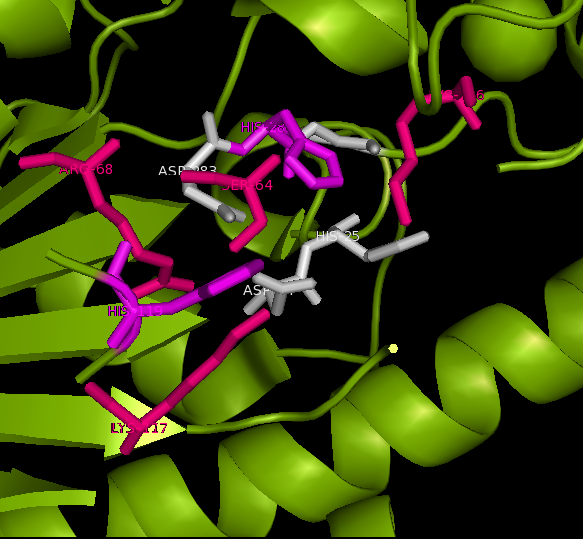
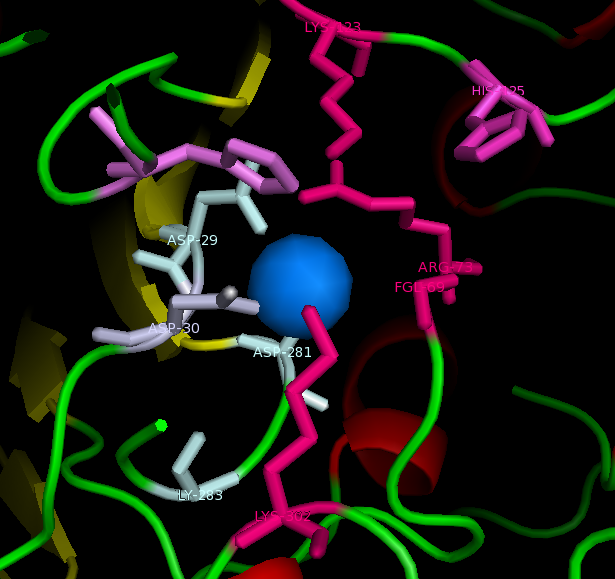
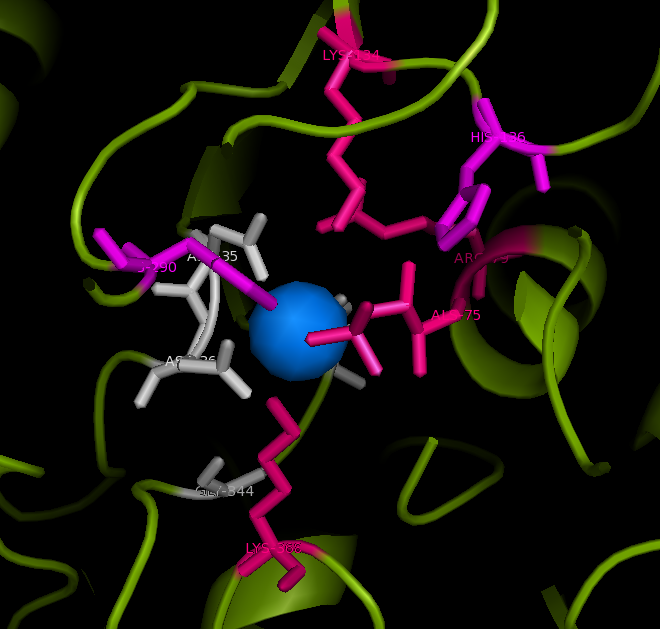
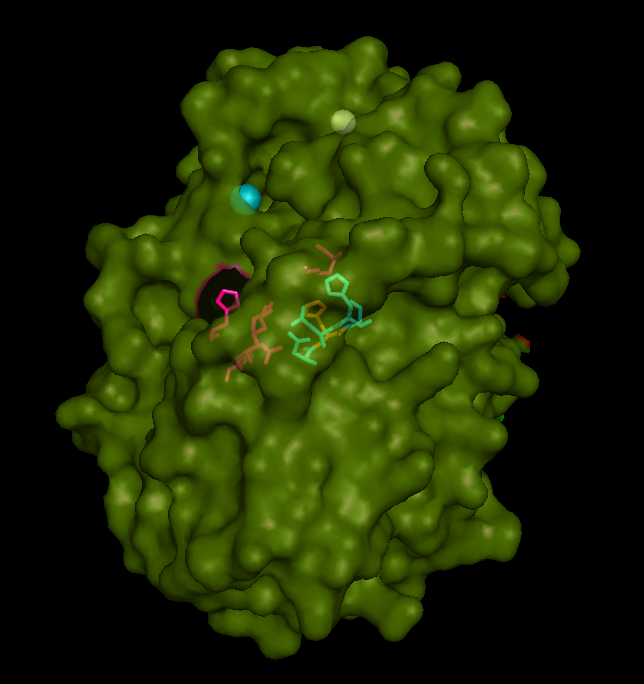
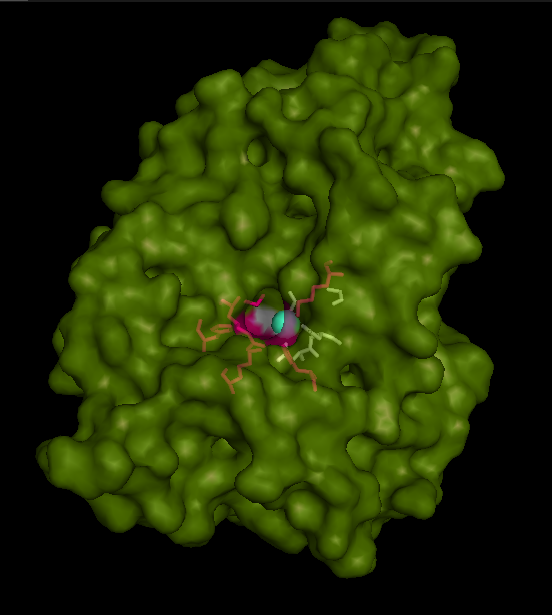
Active site and surface architecture
Possible function and likely substrates of ASK
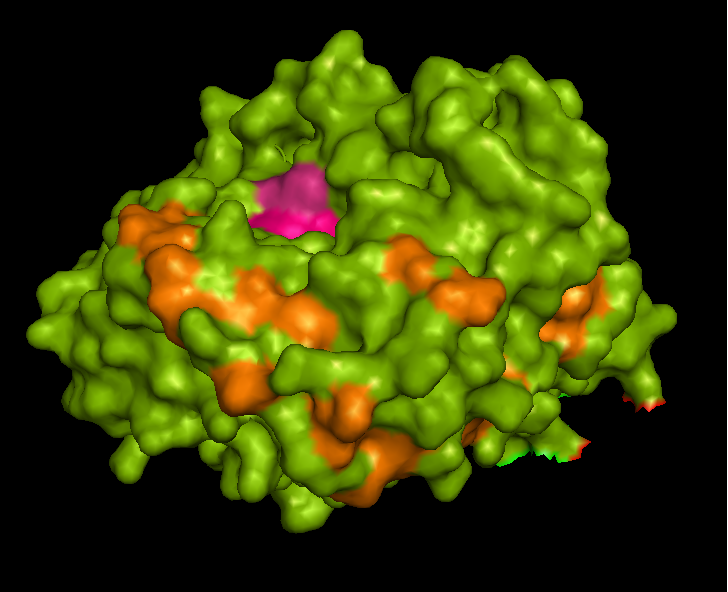
ASA is a water soluble enzyme found in lysosomes, where the catalytic site is closer to the surface and substrate-entry path is narrower and wider in contrast to that of STS. Structural comparison shows ASK catalsytic site architecture is much similar to that of ASA, eventhough subcellular localization is very different. ASA binds to membrane lipid sulphatides and show a number of hydrophibic patches near the catalytic site. However an exact substrate binding site is not defined. ASK structure also show number of hydrophobic residues on the surface (Figure 11) indicating the hydrophobic nature of the substrate it binds.
Multiple sequence alignment
- The multiple sequence alignment constructed in clustalx shows similiarity extended across the entire sequences, especially observed in N-termainal. The N-terminal showed conserved regions of amino acids containing arginine and histidine residues, which have found to be involved in the assembly of active sites of most arylsulfatases.
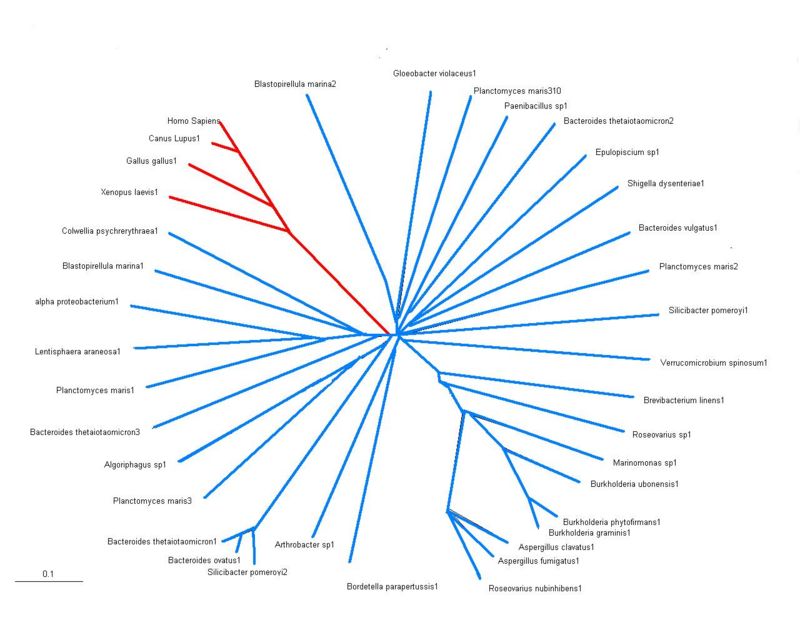
Phylogeny Tree
- There are 2 main groups shown on the tree that has been constructed using results from BLASTP results, shown in the red is eukayotes and in the blue are all the bacterial species. Significant conservation among all the different species are seen suggesting sulfatases are members of an evolutionary conserved gene family sharing a common ancestor. However, the bacteria and lower eukaryotes show fewer sulfatase genes compared with higher eukaryotes such as homo sapiens. This may suggest a common ancestor was more closely related to sulfatases present today in lower sulfatases.